Cutting Edge: Circulating Exosomes with COVID Spike Protein Are Induced by BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of Antibodies: A Novel Mechanism for Immune Activation by mRNA Vaccines
- PMID: 34654691
- PMCID: PMC11073804
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100637
Cutting Edge: Circulating Exosomes with COVID Spike Protein Are Induced by BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of Antibodies: A Novel Mechanism for Immune Activation by mRNA Vaccines
Abstract
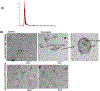
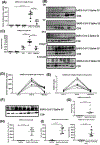
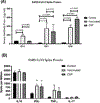
Severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes severe acute respiratory syndrome. mRNA vaccines directed at the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein resulted in development of Abs and protective immunity. To determine the mechanism, we analyzed the kinetics of induction of circulating exosomes with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and Ab following vaccination of healthy individuals. Results demonstrated induction of circulating exosomes expressing spike protein on day 14 after vaccination followed by Abs 14 d after the second dose. Exosomes with spike protein, Abs to SARS-CoV-2 spike, and T cells secreting IFN-γ and TNF-α increased following the booster dose. Transmission electron microscopy of exosomes also demonstrated spike protein Ags on their surface. Exosomes with spike protein and Abs decreased in parallel after four months. These results demonstrate an important role of circulating exosomes with spike protein for effective immunization following mRNA-based vaccination. This is further documented by induction of humoral and cellular immune responses in mice immunized with exosomes carrying spike protein.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. All authors have reviewed and approved the manuscript and have contributed in a substantial and intellectual manner to the work.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response to Comment on "Cutting Edge: Circulating Exosomes with COVID Spike Protein Are Induced by BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of Antibodies: A Novel Mechanism for Immune Activation by mRNA Vaccines".J Immunol. 2022 Apr 15;208(8):1833-1834. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101067. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418502 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on "Cutting Edge: Circulating Exosomes with COVID Spike Protein Are Induced by BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of Antibodies: A Novel Mechanism for Immune Activation by mRNA Vaccines".J Immunol. 2022 Apr 15;208(8):1833. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101082. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418503 No abstract available.
-
Comment on "Cutting Edge: Circulating Exosomes with COVID Spike Protein Are Induced by BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of Antibodies: A Novel Mechanism for Immune Activation by mRNA Vaccines".J Immunol. 2024 Mar 1;212(5):753. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300425. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38377475 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S, Novak R, Diemert D, Spector SA, Rouphael N, Creech CB, McGettigan J, Khetan S, Segall N, Solis J, Brosz A, Fierro C, Schwartz H, Neuzil K, Corey L, Gilbert P, Janes H, Follmann D, Marovich M, Mascola J, Polakowski L, Ledgerwood J, Graham BS, Bennett H, Pajon R, Knightly C, Leav B, Deng W, Zhou H, Han S, Ivarsson M, Miller J, Zaks T, and C. S. Group. 2021. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N Engl J Med 384: 403–416. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walsh EE, Frenck RW Jr., Falsey AR, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, Neuzil K, Mulligan MJ, Bailey R, Swanson KA, Li P, Koury K, Kalina W, Cooper D, Fontes-Garfias C, Shi PY, Tureci O, Tompkins KR, Lyke KE, Raabe V, Dormitzer PR, Jansen KU, Sahin U, and Gruber WC. 2020. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. N Engl J Med 383: 2439–2450. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Teo SP 2021. Review of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273. J Pharm Pract: 8971900211009650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

