Genetic investigation of fibromuscular dysplasia identifies risk loci and shared genetics with common cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 34654805
- PMCID: PMC8521585
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26174-2
Genetic investigation of fibromuscular dysplasia identifies risk loci and shared genetics with common cardiovascular diseases
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Genetic investigation of fibromuscular dysplasia identifies risk loci and shared genetics with common cardiovascular diseases.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 20;13(1):2251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29921-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35443759 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
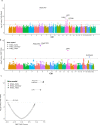
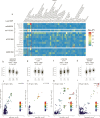
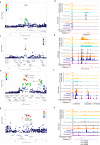
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is an arteriopathy associated with hypertension, stroke and myocardial infarction, affecting mostly women. We report results from the first genome-wide association meta-analysis of six studies including 1556 FMD cases and 7100 controls. We find an estimate of SNP-based heritability compatible with FMD having a polygenic basis, and report four robustly associated loci (PHACTR1, LRP1, ATP2B1, and LIMA1). Transcriptome-wide association analysis in arteries identifies one additional locus (SLC24A3). We characterize open chromatin in arterial primary cells and find that FMD associated variants are located in arterial-specific regulatory elements. Target genes are broadly involved in mechanisms related to actin cytoskeleton and intracellular calcium homeostasis, central to vascular contraction. We find significant genetic overlap between FMD and more common cardiovascular diseases and traits including blood pressure, migraine, intracranial aneurysm, and coronary artery disease.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H.L.G., S.K.G., J.O., and J.C.S. are non-compensated members of the Medical Advisory Board of the FMD Society of America (FMDSA). S.K.G. is a non-compensated member of the Scientific Advisory Board of SCAD Alliance. Both are non-profit organizations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The complex genetic basis of fibromuscular dysplasia, a systemic arteriopathy associated with multiple forms of cardiovascular disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Aug 31;136(16):1241-1255. doi: 10.1042/CS20210990. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36043395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PHACTR1 Is a Genetic Susceptibility Locus for Fibromuscular Dysplasia Supporting Its Complex Genetic Pattern of Inheritance.PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 28;12(10):e1006367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006367. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27792790 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics of Fibromuscular Dysplasia.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 21;19(5):1526. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051526. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29883369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome 1q21.2 and additional loci influence risk of spontaneous coronary artery dissection and myocardial infarction.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 4;11(1):4432. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17558-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32887874 Free PMC article.
-
Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Are Dimorphic Sex-Specific Diseases With Shared Complex Genetic Architecture.Circ Genom Precis Med. 2022 Dec;15(6):e003496. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.121.003496. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2022. PMID: 36374587 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Arterial dissections: Common features and new perspectives.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Dec 6;9:1055862. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1055862. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36561772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRP1 Repression by SNAIL Results in ECM Remodeling in Genetic Risk for Vascular Diseases.Circ Res. 2024 Nov 8;135(11):1084-1097. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325269. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 39355906 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific genetic architecture of blood pressure.Nat Med. 2024 Mar;30(3):818-828. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02858-2. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 38459180 Free PMC article.
-
The complex genetic basis of fibromuscular dysplasia, a systemic arteriopathy associated with multiple forms of cardiovascular disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Aug 31;136(16):1241-1255. doi: 10.1042/CS20210990. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36043395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of migraine: where are we now?J Headache Pain. 2023 Feb 20;24(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01547-8. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 36800925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health, O. World Health Statistics 2020: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

