Activation of whole body by high levels of polyamine intake in rats
- PMID: 34654958
- PMCID: PMC8592999
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-021-03079-4
Activation of whole body by high levels of polyamine intake in rats
Abstract
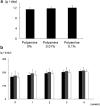
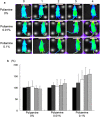
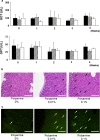
Polyamines are important to the survival and activation of organs and tissues via a homeostatic cell-metabolic process, and the polyamine content in cytoplasm decreases with aging. Decreases in cellular polyamine have been known to augment mutagenesis and cell death. Thus, supplementary polyamine in food is important to the prevention of aging. Here we show the anti-aging effects of oral intake of polyamine using luciferase-transgenic rats. Healthy rats, 10-12 weeks old, were given foods containing 0.01% and 0.1% (w/w) of polyamine, as compared a control food without polyamine, for 4 weeks. Using a bioimaging system, the photon intensities seen in the whole bodies and livers of rats consuming 0.1% of polyamine in food were stronger than those in rats consuming 0.01% and 0% of polyamine. However, there were no differences between groups in other characteristics, such as liver damage and body weight. In conclusion, we found that polyamine intake can activate cells throughout the whole body, providing an anti-aging effect.
Keywords: Anti-aging; Living imaging; Oral intake; Polyamine; Transgenic rat.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Author T. Ijichi has been a visiting Collaborative Researcher at Jichi Medical University and a Chief Manager of R&D Group to Division of Functional Foods, Combi Corporation. (Saitama, Japan) from 2010. In this research result was patented (No. 5909173 and No. 6117963).
Figures

References
-
- Agostinelli E, Tempera G, Viceconte N, Saccoccio S, Battaglia V, Grancara S, Toninello A, Stevanato R. Potential anticancer application of polyamine oxidation products formed by amine oxidase: a new therapeutic approach. Amino Acids. 2010;38:353–368. - PubMed
-
- Alemany J, de la Cruz MJ, Roncero I, Miquel J. Effects of aging on respiration, ATP levels and calcium transport in rat liver mitochondria. Response to theophylline. Exp Gerontol. 1988;23:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Anand KV, Mohamed Jaabir MS, Thomas PA, Geraldine P. Protective role of chrysin against oxidative stress in d-galactose-induced aging in an experimental rat model. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2012;12:741–750. - PubMed
-
- Bachrach U, Ash I, Abu-Elheiga L, Hershkovitz M, Loyter A. Fusion-mediated microinjection of active amine and diamine oxidases into cultured cells: effect on protein and DNA synthesis in chick embryo fibroblasts and in glioma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987;131:92–98. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

