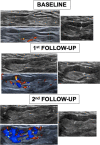
Unilateral axillary adenopathy induced by COVID-19 vaccine: US follow-up evaluation
- PMID: 34655312
- PMCID: PMC8520081
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-021-08309-7
Unilateral axillary adenopathy induced by COVID-19 vaccine: US follow-up evaluation
Abstract
Objectives: This study was conducted in order to investigate COVID-19 vaccine influence on unilateral axillary lymph nodes, comparing nodal basal features with their characteristics after the first and second vaccination dose.
Methods: Ninety-one volunteer employees from our center who participated in the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccination campaign were prospectively recruited. A total of three axillary ultrasound evaluations of the ipsilateral vaccinated arm were performed: before vaccination, the week after the first dose and the week after the second dose. The following findings were recorded: the total number of visible nodes, the maximum measurements of the diameter and cortex, Bedi's classification, and color Doppler evaluation. The collected data were compared using paired-sample Student's t-test for quantitative continuous variables and Wilcoxon rank-sum test for ordinal variables. Additional analyses were performed after classifying patients according to the previous history of COVID-19 disease. Differences among both groups were evaluated with the Mann-Whitney U test. Variables with a p value < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
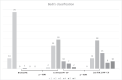
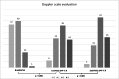
Results: Comparative analyses between the three US examinations showed a statistically significant augmentation of total visible nodes, maximum diameter, cortical thickness, grade of Bedi's classification, and Doppler signal (p < 0.001). Analyses between patients with and without previous COVID-19 infection showed a higher lymph node response in naïve patients compared to those who were previously infected.
Conclusions: According to our results, both doses of COVID-19 vaccine induced an increase of all axillary lymph node parameters with statistically significant differences, especially in coronavirus-naïve patients.
Key points: • Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine induces a high incidence of ipsilateral axillary lymphadenopathy. • US scan identified an increase of all lymph nodes parameters, especially in coronavirus-naïve patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Ultrasound; Unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy; mRNA vaccine.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures



References
-
- WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. (n.d). Retrieved July 1, 2021, from https://covid19.who.int/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

