Hepatocyte-Specific Deletion of HIF2α Prevents NASH-Related Liver Carcinogenesis by Decreasing Cancer Cell Proliferation
- PMID: 34655812
- PMCID: PMC8688724
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.10.002
Hepatocyte-Specific Deletion of HIF2α Prevents NASH-Related Liver Carcinogenesis by Decreasing Cancer Cell Proliferation
Abstract
Background & aims: Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are involved in chronic liver disease progression. We previously showed that hepatocyte HIF-2α activation contributed significantly to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in experimental animals and human patients. In this study, using an appropriate genetic murine model, we mechanistically investigated the involvement of hepatocyte HIF-2α in experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-related carcinogenesis.
Methods: The role of HIF-2α was investigated by morphologic, cellular, and molecular biology approaches in the following: (1) mice carrying hepatocyte-specific deletion of HIF-2α (HIF-2α-/- mice) undergoing a NASH-related protocol of hepatocarcinogenesis; (2) HepG2 cells stably transfected to overexpress HIF-2α; and (3) liver specimens from NASH patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
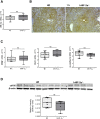
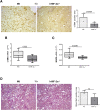
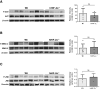
Results: Mice carrying hepatocyte-specific deletion of HIF-2α (hHIF-2α-/-) showed a significant decrease in the volume and number of liver tumors compared with wild-type littermates. These effects did not involve HIF-1α changes and were associated with a decrease of cell proliferation markers proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Ki67. In both human and rodent nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-related tumors, HIF-2α levels were strictly associated with hepatocyte production of SerpinB3, a mediator previously shown to stimulate liver cancer cell proliferation through the Hippo/Yes-associated protein (YAP)/c-Myc pathway. Consistently, we observed positive correlations between the transcripts of HIF-2α, YAP, and c-Myc in individual hepatocellular carcinoma tumor masses, while HIF-2α deletion down-modulated c-Myc and YAP expression without affecting extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and AKT-dependent signaling. In vitro data confirmed that HIF-2α overexpression induced HepG2 cell proliferation through YAP-mediated mechanisms.
Conclusions: These results indicate that the activation of HIF-2α in hepatocytes has a critical role in liver carcinogenesis during NASH progression, suggesting that HIF-2α-blocking agents may serve as novel putative therapeutic tools.
Keywords: HIF-2α; Hepatocellular Carcinoma; NAFLD; NASH.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures












Comment in
-
HIF2α Activation in NASH: A New Force Pushing Toward HCC.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;13(2):678-680. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34848185 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Younossi Z., Tacke F., Arrese M., Chander Sharma B., Mostafa I., Bugianesi E., Wong V.W.-S., Yilmaz Y., George J., Fan J., Vos M. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;69:2672–2682. - PubMed
-
- McPherson S., Hardy T., Henderson E., Burt A.D., Day C.P., Anstee Q.M. Evidence of NAFLD progression from steatosis to fibrosing-steatohepatitis using paired biopsies: implications for prognosis and clinical management. J Hepatol. 2015;62:1148–1155. - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z.M., Golabi P., de Avila L., Minhui Paik J., Srishord M., Fukui N., Qiu Y., Burns L., Afendy A., Nader F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2019;71:793–801. - PubMed
-
- Torres D.M., Harrison S.A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and noncirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma: fertile soil. Semin Liver Dis. 2012;32:30–38. - PubMed
-
- Younes R., Bugianesi E. Should we undertake surveillance for HCC in patients with NAFLD? J Hepatol. 2018;68:326–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

