State-of-the-art review - A review on snake venom-derived antithrombotics: Potential therapeutics for COVID-19-associated thrombosis?
- PMID: 34656540
- PMCID: PMC8514616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.015
State-of-the-art review - A review on snake venom-derived antithrombotics: Potential therapeutics for COVID-19-associated thrombosis?
Abstract
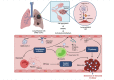
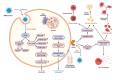
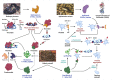
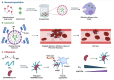
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent responsible for the Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has infected over 185 million individuals across 200 countries since December 2019 resulting in 4.0 million deaths. While COVID-19 is primarily associated with respiratory illnesses, an increasing number of clinical reports indicate that severely ill patients often develop thrombotic complications that are associated with increased mortality. As a consequence, treatment strategies that target COVID-associated thrombosis are of utmost clinical importance. An array of pharmacologically active compounds from natural products exhibit effects on blood coagulation pathways, and have generated interest for their potential therapeutic applications towards thrombotic diseases. In particular, a number of snake venom compounds exhibit high specificity on different blood coagulation factors and represent excellent tools that could be utilized to treat thrombosis. The aim of this review is to provide a brief summary of the current understanding of COVID-19 associated thrombosis, and highlight several snake venom compounds that could be utilized as antithrombotic agents to target this disease.
Keywords: Anticoagulant; Antiplatelet; Antithrombotic; COVID-19; Snake venom; Thrombosis.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Pneumonia of unknown cause – China. Disease outbreak news, 5 January 2020. Geneva. 2020. www.who.int/csr/don/05january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-china/en/
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y.M., Wang W., Song Z.G., Hu Y., Tao Z.W., Tian J.H., Pei Y.Y., Yuan M.L., Zhang Y.L., Dai F.H., Liu Y., Wang Q.M., Zheng J.J., Xu L., Holmes E.C., Zhang Y.Z. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;579(7798):265–269. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ma J. Coronavirus: China’s first confirmed Covid-19 case traced back to November 17, South China Morning Post, 13 March 2020. 2020. www.scmp.com/news/china/society/article/3074991/coronavirus-chinas-first...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

