Detection of COVID-19 from voice, cough and breathing patterns: Dataset and preliminary results
- PMID: 34656870
- PMCID: PMC8513517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104944
Detection of COVID-19 from voice, cough and breathing patterns: Dataset and preliminary results
Abstract
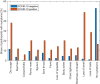
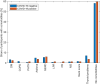
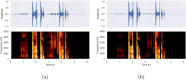
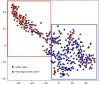
COVID-19 heavily affects breathing and voice and causes symptoms that make patients' voices distinctive, creating recognizable audio signatures. Initial studies have already suggested the potential of using voice as a screening solution. In this article we present a dataset of voice, cough and breathing audio recordings collected from individuals infected by SARS-CoV-2 virus, as well as non-infected subjects via large scale crowdsourced campaign. We describe preliminary results for detection of COVID-19 from cough patterns using standard acoustic features sets, wavelet scattering features and deep audio embeddings extracted from low-level feature representations (VGGish and OpenL3). Our models achieve accuracy of 88.52%, sensitivity of 88.75% and specificity of 90.87%, confirming the applicability of audio signatures to identify COVID-19 symptoms. We furthermore provide an in-depth analysis of the most informative acoustic features and try to elucidate the mechanisms that alter the acoustic characteristics of coughs of people with COVID-19.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; COVID-19; Cough; Digital biomarker; Voice.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sanders J., Monogue M., Jodlowski T., Cutrell J. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020;323(18):1824–1836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

