Biosimilar SB11 versus reference ranibizumab in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: 1-year phase III randomised clinical trial outcomes
- PMID: 34656987
- PMCID: PMC9985746
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2021-319637
Biosimilar SB11 versus reference ranibizumab in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: 1-year phase III randomised clinical trial outcomes
Abstract
Background/aims: To provide longer-term data on efficacy, safety, immunogenicity and pharmacokinetics (PK) of ranibizumab biosimilar SB11 compared with the reference ranibizumab (RBZ) in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD).
Methods: Setting: Multicentre. Design: Randomised, double-masked, parallel-group, phase III equivalence study. Patient population: ≥50 years old participants with nAMD (n=705), one 'study eye'.
Intervention: 1:1 randomisation to monthly intravitreal injection of 0.5 mg SB11 or RBZ. Main outcome measures: Visual efficacy endpoints, safety, immunogenicity and PK up to 52 weeks.
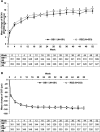
Results: Baseline and disease characteristics were comparable between treatment groups. Of 705 randomised participants (SB11: n=351; RBZ: n=354), 634 participants (89.9%; SB11: n=307; RBZ: n=327) completed the study until week 52. Previously reported equivalence in primary efficacy remained stable up to week 52 and were comparable between SB11 and RBZ. The adjusted treatment difference between SB11 and RBZ in full analysis set at week 52 of change from baseline in best-corrected visual acuity was -0.6 letters (90% CI -2.1 to 0.9) and of change from baseline in central subfield thickness was -14.9 µm (95% CI -25.3 to -4.5). The incidence of ocular treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) (SB11: 32.0% vs RBZ: 29.7%) and serious ocular TEAE (SB11: 2.9% vs RBZ: 2.3%) appeared comparable between treatment groups, and no new safety concerns were observed. The PK and immunogenicity profiles were comparable, with a 4.2% and 5.5% cumulative incidence of antidrug antibodies up to week 52 for SB11 and RBZ, respectively.
Conclusions: Longer-term results of this study further support the biosimilarity established between SB11 and RBZ.
Keywords: degeneration; macula; neovascularisation; retina.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: NB reported receiving grants from Samsung Bioepis to Johns Hopkins University during the conduct of the study and receiving grants from Bayer, Biogen, F. Hoffman-LaRoche, Novartis, Regeneron outside the submitted work. JS is a consultant for Bayer and Zeiss and received lecture fee from Bayer. AV received grants from Novartis, Bayer, Opthtotec/Iveric Bio, Samsung Bioepis, Amgen, Qilu, Chengdu Kanghong, Roche, Mylan, Receptos, Shire, Panoptica, Xbrain, Formycon, Genentech, Bioeq, Allergan, Thrombogenics, Regeneron, Alcon and Clearside Biomedical and is a consultant for and an advisory board member of Novartis, Bayer, Allergan, Bausch & Lomb, Medicontour and Zeiss. AP is a consultant for Roche, Bayer and Novartis received travel grants from Novartis and his company has received investigator fees from Samsung Bioepis, Roche, Iveric Bio, Allergan and Chengdu Kanghong. GV is a consultant for Alcon and Novartis, received travel grants from Novartis and Medicontur and his department has been involved in the conduct of several studies sponsored by Samsung Bioepis, Allergan, Chengdu Kanghong, Xbrane Biopharma, Thrombogenics, Amgen, Qilu, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Bayer, Ophtotec, Novartis and Regeneron. YHY is a consultant for Alcon, Allergan Bayer and Roche, is Board Member of Allergan, Bayer and Roche, received grants from Allergan, Samsung Bioepis, Bayer, Novartis and Roche and received lecture fee from Allergan, Bayer and Roche. TP received travel grants from Alcon, Novartis and Bausch & Lomb and his department has been involved in the conduct of several studies sponsored by Mylan, Samsung Bioepis, Xbrane Biopharma, Kanghong Pharmaceuticals, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Allergan, Bayer and Ophtotec. SJW is a consultant for Samsung Bioepis, Janssen, Allergan, Novartis, Curacle, Novelty Nobility, Alteogen, Philophos, Panols Bioscience, is equity owner of Retimark and Panolos Bioscience, is Board Member of Novartis and Novelty Nobility, received grants from Samsung Bioepis, Novelty Nobility, Novartis, Abbvie, Alteogen and Curacle and received lecture fee from Novartis, Bayer, Allergan, Abbvie, Alcon and Taejoon. Inkyung Oh, Hansol Jeong and Mercy Yeeun Kim are employees of Samsung Bioepis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
