Prognostic impact of chromosomal abnormalities and copy number alterations in adult B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a UKALL14 study
- PMID: 34657128
- PMCID: PMC8885405
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-021-01448-2
Prognostic impact of chromosomal abnormalities and copy number alterations in adult B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a UKALL14 study
Abstract
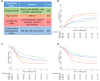
Chromosomal abnormalities are established prognostic markers in adult ALL. We assessed the prognostic impact of established chromosomal abnormalities and key copy number alterations (CNA) among 652 patients with B-cell precursor ALL treated on a modern MRD driven protocol. Patients with KMT2A-AFF1, complex karyotype (CK) and low hypodiploidy/near-triploidy (HoTr) had high relapse rates 50%, 60% & 53% and correspondingly poor survival. Patients with BCR-ABL1 had an outcome similar to other patients. JAK-STAT abnormalities (CRLF2, JAK2) occurred in 6% patients and were associated with a high relapse rate (56%). Patients with ABL-class fusions were rare (1%). A small group of patients with ZNF384 fusions (n = 12) had very good survival. CNA affecting IKZF1, CDKN2A/B, PAX5, BTG1, ETV6, EBF1, RB1 and PAR1 were assessed in 436 patients. None of the individual deletions or profiles were associated with survival, either in the cohort overall or within key subgroups. Collectively these data indicate that primary genetic abnormalities are stronger prognostic markers than secondary deletions. We propose a revised UKALL genetic risk classification based on key established chromosomal abnormalities: (1) very high risk: CK, HoTr or JAK-STAT abnormalities; (2) high risk: KMT2A fusions; (3) Tyrosine kinase activating: BCR-ABL1 and ABL-class fusions; (4) standard risk: all other patients.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bassan R, Bourquin JP, DeAngelo DJ, Chiaretti S. New approaches to the management of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018: JCO2017773648. - PubMed
-
- Moorman AV, Harrison CJ, Buck GA, Richards SM, Secker-Walker LM, Martineau M, et al. Karyotype is an independent prognostic factor in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): analysis of cytogenetic data from patients treated on the Medical Research Council (MRC) UKALLXII/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2993 Trial. Blood. 2007;109:3189–97. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-051912. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fielding AK, Rowe JM, Richards SM, Buck G, Moorman AV, Durrant IJ, et al. Prospective outcome data on 267 unselected adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia confirms superiority of allogeneic transplantation over chemotherapy in the pre-imatinib era: results from the International ALL Trial MRC UKALLXII/ECOG2993. Blood. 2009;113:4489–96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-199380. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marks DI, Moorman AV, Chilton L, Paietta E, Enshaie A, DeWald G, et al. The clinical characteristics, therapy and outcome of 85 adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and t(4;11)(q21;q23)/MLL-AFF1 prospectively treated in the UKALLXII/ECOG2993 trial. Haematologica. 2013;98:945–52. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.081877. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Patel B, Rai L, Buck G, Richards SM, Mortuza Y, Mitchell W, et al. Minimal residual disease is a significant predictor of treatment failure in non T-lineage adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: final results of the international trial UKALL XII/ECOG2993. Br J Haematol. 2010;148:80–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07941.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

