MCPIP1 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activity and modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting miRNAs
- PMID: 34657130
- PMCID: PMC8677621
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-021-02062-3
MCPIP1 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activity and modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting miRNAs
Abstract
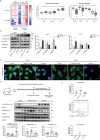
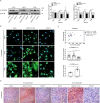
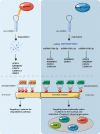
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) refers to the acquisition of mesenchymal properties in cells participating in tumor progression. One hallmark of EMT is the increased level of active β-catenin, which can trigger the transcription of Wnt-specific genes responsible for the control of cell fate. We investigated how Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1-Induced Protein-1 (MCPIP1), a negative regulator of inflammatory processes, affects EMT in a clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cell line, patient tumor tissues and a xenotransplant model. We showed that MCPIP1 degrades miRNAs via its RNase activity and thus protects the mRNA transcripts of negative regulators of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway from degradation, which in turn prevents EMT. Mechanistically, the loss of MCPIP1 RNase activity led to the upregulation of miRNA-519a-3p, miRNA-519b-3p, and miRNA-520c-3p, which inhibited the expression of Wnt pathway inhibitors (SFRP4, KREMEN1, CXXC4, CSNK1A1 and ZNFR3). Thus, the level of active nuclear β-catenin was increased, leading to increased levels of EMT inducers (SNAI1, SNAI2, ZEB1 and TWIST) and, consequently, decreased expression of E-cadherin, increased expression of mesenchymal markers, and acquisition of the mesenchymal phenotype. This study revealed that MCPIP1 may act as a tumor suppressor that prevents EMT by stabilizing Wnt inhibitors and decreasing the levels of active β-catenin and EMT inducers.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
SOX6 represses tumor growth of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by HMG domain-dependent regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Mol Carcinog. 2020 Oct;59(10):1159-1173. doi: 10.1002/mc.23246. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Mol Carcinog. 2020. PMID: 32794610
-
Novel long noncoding RNA OTUD6B-AS1 indicates poor prognosis and inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma proliferation via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Mol Cancer. 2019 Jan 22;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0942-1. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30670025 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-506 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by down-regulating LHX2.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 21;38(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1023-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Sep 30;40(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02113-3. PMID: 30791932 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Interplay between microRNAs and WNT/β-catenin signalling pathway regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2015 Aug;51(12):1638-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.04.021. Epub 2015 May 26. Eur J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26025765 Review.
-
ΔNp63α and microRNAs: leveraging the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2114-2129. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13797. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27924063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid Hormone Induces Oral Cancer Growth via the PD-L1-Dependent Signaling Pathway.Cells. 2022 Sep 29;11(19):3050. doi: 10.3390/cells11193050. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231010 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular landscape of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 14;16(1):524. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02228-5. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40227498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Frizzled-7-targeting antibody (SHH002-hu1) potently suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer via Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Cancer Sci. 2023 May;114(5):2109-2122. doi: 10.1111/cas.15721. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36625184 Free PMC article.
-
TTC13 expression and STAT3 activation may form a positive feedback loop to promote ccRCC progression.PeerJ. 2023 Oct 30;11:e16316. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16316. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37927783 Free PMC article.
-
NEK2 Serves as a Novel Biomarker and Enhances the Tumorigenicity of Clear-CellRenal-Cell Carcinoma by Activating WNT/β-Catenin Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Sep 29;2022:1890823. doi: 10.1155/2022/1890823. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9876715. doi: 10.1155/2023/9876715. PMID: 36212952 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Behrens J, Jerchow BA, Würtele M, Grimm J, Asbrand C, Wirtz R, et al. Functional interaction of an axin homolog, conductin, with beta-catenin, APC, and GSK3beta. Science. 1998;280:596–9. - PubMed
-
- Kurose K, Sakaguchi M, Nasu Y, Ebara S, Kaku H, Kariyama R, et al. Decreased expression of REIC/Dkk-3 in human renal clear cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2004;171:1314–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

