Recent progress of iPSC technology in cardiac diseases
- PMID: 34657219
- PMCID: PMC8522114
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-021-03172-3
Recent progress of iPSC technology in cardiac diseases
Abstract
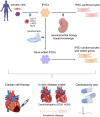
It has been nearly 15 years since the discovery of human-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). During this time, differentiation methods to targeted cells have dramatically improved, and many types of cells in the human body can be currently generated at high efficiency. In the cardiovascular field, the ability to generate human cardiomyocytes in vitro with the same genetic background as patients has provided a great opportunity to investigate human cardiovascular diseases at the cellular level to clarify the molecular mechanisms underlying the diseases and discover potential therapeutics. Additionally, iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes have provided a powerful platform to study drug-induced cardiotoxicity and identify patients at high risk for the cardiotoxicity; thus, accelerating personalized precision medicine. Moreover, iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes can be sources for cardiac cell therapy. Here, we review these achievements and discuss potential improvements for the future application of iPSC technology in cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Cardiomyocyte; Differentiation into subtypes; Disease modeling; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Maturation.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
YY received research funding from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Ando H, Yoshinaga T, Yamamoto W, Asakura K, Uda T, Taniguchi T, Ojima A, Shinkyo R, Kikuchi K, Osada T, Hayashi S, Kasai C, Miyamoto N, Tashibu H, Yamazaki D, Sugiyama A, Kanda Y, Sawada K, Sekino Y. A new paradigm for drug-induced torsadogenic risk assessment using human ips cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2017;84:111–127. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2016.12.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baek M, DiMaio F, Anishchenko I, Dauparas J, Ovchinnikov S, Lee GR, Wang J, Cong Q, Kinch LN, Schaeffer RD, Millan C, Park H, Adams C, Glassman CR, DeGiovanni A, Pereira JH, Rodrigues AV, van Dijk AA, Ebrecht AC, Opperman DJ, Sagmeister T, Buhlheller C, Pavkov-Keller T, Rathinaswamy MK, Dalwadi U, Yip CK, Burke JE, Garcia KC, Grishin NV, Adams PD, Read RJ, Baker D. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science. 2021;373:871–876. doi: 10.1126/science.abj8754. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources