Knockout of Macula Densa Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Increases Blood Pressure in db/db Mice
- PMID: 34657443
- PMCID: PMC8651058
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17643
Knockout of Macula Densa Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Increases Blood Pressure in db/db Mice
Abstract
[Figure: see text].
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; glomerular filtration rate; hemodynamics; hypertension; kidney; nitric oxide; nitric oxide synthase.
Figures
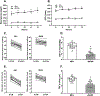
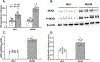
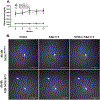
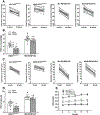
References
-
- Gillespie CD, Hurvitz KA, Centers for Disease C, Prevention. Prevalence of hypertension and controlled hypertension - united states, 2007-2010. MMWR Suppl. 2013;62:144–148 - PubMed
-
- Hypertension in diabetes study (hds): I. Prevalence of hypertension in newly presenting type 2 diabetic patients and the association with risk factors for cardiovascular and diabetic complications. J Hypertens. 1993;11:309–317 - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR, Epstein M, Frohlich ED. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: An update. Hypertension. 2001;37:1053–1059 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

