Symptom Prevalence and Place of Death Preference in Advanced Cancer Patients: Factors Associated With the Achievement of Home Death
- PMID: 34657488
- PMCID: PMC9210115
- DOI: 10.1177/10499091211048767
Symptom Prevalence and Place of Death Preference in Advanced Cancer Patients: Factors Associated With the Achievement of Home Death
Abstract
Objectives: Achievement of patients' preferred place of death is recognized as a component of a good death. This study aimed to investigate the symptom burden in advanced cancer patients, achievement of their place of death preferences and factors associated with home death.
Methods: In this retrospective review of 287 patient deaths, we examined patients' symptom prevalence, preferred and actual place of death and achievement of their place of death preferences using descriptive statistics. Associations between patient factors, home death preference and actual home death were further analyzed using multivariate logistic regression.
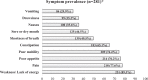
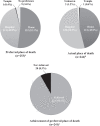
Results: The most prevalent symptoms were weakness, pain and poor appetite, with a mean of 5.77(SD: 2.37) symptoms per patient. The median interval from palliative care referral to death was 21 (IQR: 74) days. Of the 253 patients with documented place of death preference, 132 (52.1%) preferred home death, 111(43.9%) preferred hospital death, 1 (0.4%) preferred to die at a temple and 9(3.6%) expressed no preference. Overall, 221 of 241(91.7%) patients with known actual place of death achieved their preference. Older patients were more likely to prefer home death (OR 1.021; 95% CI 1.004-1.039, p = 0.018) and die at home (OR 1.023; 95% CI 1.005-1.041, p = 0.014). Gender, marital status, cancer diagnosis and symptoms were not associated with preference for or actual home death.
Conclusion: Despite a high symptom burden, most patients preferred and achieved a home death. Late palliative care referral and difficult symptom management contributed to failure to fulfill home death preference. Preference for home death should be considered when managing terminally ill geriatric patients.
Keywords: cancer; geriatrics; home death; palliative care; place of death preference; symptom.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Department of Health. End of Life Care Strategy—Promoting High Quality Care of All Adults at the End of Life. Department of Health; 2008.
-
- Brogaard T, Neergaard MA, Sokolowski I, Olesen F, Jensen AB. Congruence between preferred and actual place of care and death among Danish cancer patients. Palliat Med. 2013;27(2):155–164. - PubMed
-
- Hunt KJ, Shlomo N, Addington-Hall J. End-of-life care and achieving preferences for place of death in England: results of a population-based survey using the VOICES-SF questionnaire. Palliat Med. 2014;28(5):412–421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

