Recognition of double-stranded DNA using LNA-modified toehold Invader probes
- PMID: 34657934
- PMCID: PMC8625219
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ob01888d
Recognition of double-stranded DNA using LNA-modified toehold Invader probes
Abstract
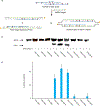
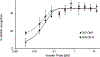
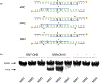
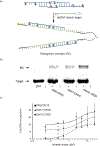
Development of molecules capable of binding to specific sequences of double-stranded (ds) DNA continues to attract considerable interest, as this may yield useful tools for applications in life science, biotechnology, and medicine. We have previously demonstrated sequence-unrestricted of dsDNA using Invader probes, i.e., DNA duplexes that are energetically activated through incorporation of +1 interstrand zipper arrangements of O2'-intercalator-functionalized RNA monomers. Nonetheless, recognition of extended dsDNA target regions remains challenging due to the high stability of the corresponding probes. To address this, we introduce toehold Invader probes, i.e., Invader probes with 5'-single-stranded overhangs. This design provides access to probes with shortened double-stranded segments, which facilitates probe denaturation. The single-stranded overhangs can, furthermore, be modified with affinity-enhancing modifications like LNA (locked nucleic acid) monomers to additionally increase target affinity. Herein, we report the biophysical and dsDNA-targeting properties of different toehold Invader designs and compare them to conventional Invader probes. LNA-modified toehold Invader probes display promising recognition characteristics, including greatly improved affinity to dsDNA, excellent binding specificity, and fast recognition kinetics, which enabled recognition of chromosomal DNA targets that have proven refractory to recognition by conventional Invader probes. Thus, toehold Invader probes represent another step toward a robust, oligonucleotide-based approach for sequence-unrestricted dsDNA-recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS
P. J. H. is an inventor on patents pertaining to Invader probes, which have been issued to the University Idaho.
Figures

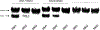

References
-
- Hari Y, Obika S and Imanishi T, Eur. J. Org. Chem, 2012, 2875–2887.
-
- Kaihatsu K, Janowski BA and Corey DR, Chem. Biol, 2004, 11, 749–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

