[A diffusion-weighted image denoising algorithm using HOSVD combined with Rician noise corrected model]
- PMID: 34658356
- PMCID: PMC8526317
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.09.16
[A diffusion-weighted image denoising algorithm using HOSVD combined with Rician noise corrected model]
Abstract
Objective: To propose a novel diffusion-weighted (DW) image denoising algorithm based on HOSVD to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of DW images and the accuracy of subsequent quantization parameters.
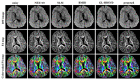
Methods: This HOSVDbased denoising method incorporated the sparse constraint and noise-correction model. The signal expectations with Rician noise were integrated into the traditional HOSVD denoising framework for direct denoising of the DW images with Rician noise. HOSVD denoising was performed directly on each local DW image block to avoid the stripe artifacts. We compared the proposed method with 4 image denoising algorithms (LR + Edge, GL-HOSVD, BM3D and NLM) to verify the effect of the proposed method.
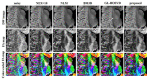
Results: The experimental results showed that the proposed method effectively reduced the noise of DW images while preserving the image details and edge structure information. The proposed algorithm was significantly better than LR +Edge, BM3D and NLM in terms of quantitative metrics of PSNR, SSIM and FA-RMSE and in visual evaluation of denoising images and FA images. GL-HOSVD obtained good denoising results but introduced stripe artifacts at a high noise level during the denoising process. In contrast, the proposed method achieved good denoising results without causing stripe artifacts.
Conclusion: This HOSVD-based denoising method allows direct processing of DW images with Rician noise without introducing artifacts and can provide accurate quantitative parameters for diagnostic purposes.
目的: 研究一种新颖的基于高阶奇异值分解(HOSVD)的扩散加权图像去噪算法, 用以提高扩散加权(DW)图像的信噪比以及后续量化参数的准确性。
方法: 我们提出一种基于HOSVD稀疏约束和Rician噪声校正模型的去噪方法, 将Rician噪声信号期望融合到传统的HOSVD去噪框架中, 从而能够直接对带有Rician噪声的DW图像进行去噪。此外, 考虑到对相似块组成的高维数组进行HOSVD去噪处理, 容易引入条形伪影, 因此本文直接对每个局部DW图像块进行HOSVD去噪, 从而解决了条形伪影问题。为了验证所提方法的有效性, 我们将本方法与低秩+边缘约束(LR+Edge)、基于全局指导下的局部高阶奇异值分解(GL-HOSVD)、基于块匹配的三维滤波(BM3D)和非局部均值(NLM)4种去噪算法进行了实验对比。
结果: 实验结果表明, 所提方法能够有效降低DW图像噪声, 同时较好的保留图像细节以及边缘结构信息。无论是从DW图像的峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性(SSIM)以及各向异性分数均方根误差定量指标, 还是从去噪图像和各向异性分数图的视觉效果来看, 本算法都要明显优于LR+Edge, BM3D和NLM。此外, GL-HOSVD虽然可以得到较好的去噪结果, 但是在高噪声水平下, 会引入条形伪影, 而本文方法不但可以得到较好的去噪结果, 并且不存在伪影问题。
结论: 本文提出了一种新颖的HOSVD去噪方法, 可以直接处理带有Rician噪声的DW图像, 并且解决了同类算法中伪影问题, 去噪效果明显, 能够为临床提供更准确的量化参数结果, 更好服务于临床影像诊断。
Keywords: HOSVD; Rician noise; diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; image denoising.
Figures




References
-
- Mori S, Barker PB. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging: its principle and applications. Anat Rec. 1999;257(3):102–9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(19990615)257:3<102::AID-AR7>3.0.CO;2-6. [Mori S, Barker PB. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging: its principle and applications[J]. Anat Rec, 1999, 257(3): 102-9.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;13(4):534–46. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1076. [Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2001, 13(4): 534-46.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kloska SP, Wintermark M, Engelhorn T, et al. Acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging: current status and future perspective. Neuroradiology. 2010;52(3):189–201. doi: 10.1007/s00234-009-0637-1. [Kloska SP, Wintermark M, Engelhorn T, et al. Acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging: current status and future perspective[J]. Neuroradiology, 2010, 52(3): 189-201.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roosendaal SD, Geurts JJ, Vrenken H, et al. Regional DTI differences in multiple sclerosis patients. Neuroimage. 2009;44(4):1397–403. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.026. [Roosendaal SD, Geurts JJ, Vrenken H, et al. Regional DTI differences in multiple sclerosis patients[J]. Neuroimage, 2009, 44 (4): 1397-403.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eriksson SH, Rugg-Gunn FJ, Symms MR, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with epilepsy and malformations of cortical development. http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/content/124/3/617.full-text.pdf. Brain. 2001;124(pt 3):617–26. [Eriksson SH, Rugg-Gunn FJ, Symms MR, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with epilepsy and malformations of cortical development[J]. Brain, 2001, 124(pt 3): 617-26.] - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
