Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Croatian solid-organ transplant recipients
- PMID: 34658649
- PMCID: PMC8495621
- DOI: 10.11613/BM.2021.030901
Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Croatian solid-organ transplant recipients
Abstract
Introduction: The data on the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in solid-organ transplant recipients (SOTRs) in Croatia is unknown. The aim of this study was to analyze the seroprevalence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Croatian SOTRs.
Materials and methods: From 7 September to 27 November 2020 (beginning of the second COVID-19 pandemic wave), a cross-sectional screening for COVID-19 was performed in the adult outpatient liver (LTRs; N = 280) and kidney transplant recipients (KTRs; N = 232). Serum samples were initially tested for SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies using a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; Vircell Microbiologists, Granada, Spain). All positive samples were confirmed using a virus neutralization test (VNT). Data on risk exposure and COVID-19 related symptoms were collected using a questionnaire.
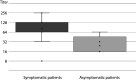
Results: The transplanted cohort's seroprevalence detected by ELISA and VNT was 20.1% and 3.1%, respectively. Neutralizing (NT) antibodies developed in 15.6% of anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA IgG positive SOTRs. The difference in seropositivity rates between LTRs and KTRs was not statistically significant (ELISA 21.1% vs. 19.0%, P = 0.554; VNT 3.6% vs. 2.6%, P = 0.082). Overall VNT positivity rates were higher in patients who reported participation in large community events (5.9% vs. 1.0%; P = 0.027) as well as in patients who reported COVID-19 related symptoms in the past six months. In addition, symptomatic VNT positive patients showed significantly higher (P = 0.031) NT antibody titers (median 128, interquartile range (IQR) = 32-128) compared to asymptomatic patients (median 16, IQR = 16-48).
Conclusions: This study showed that 15.6% of anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA positive Croatian SOTRs developed NT antibodies indicating protective immunity. Further studies are needed to determine the dynamic of NT antibodies and COVID-19 immunity duration in immunocompromised populations such as LTRs and KTRs.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 antibodies; seroprevalence; solid-organ transplant recipients.
Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Vilibić-Čavlek T, Stevanović V, Tabain I, Perić Lj, Sabadi D, Hruškar Ž, et al. Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection: preliminary results of six serology tests. Croat J Infect. 2020;40:50–4. 10.37797/ig.40.2.2 - DOI
-
- Reed LJ, Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am J Hyg. 1938;27:493–7. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118408 - DOI
-
- Vilibic-Cavlek T, Stevanovic V, Tabain I, Betica-Radic L, Sabadi D, Peric L, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 seroprevalence among personnel in the healthcare facilities of Croatia, 2020. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53:e20200458. 10.1590/0037-8682-0458-2020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous