Effects of Terlipressin on Management of Hypotensive Brain-Dead Patients Who are Potential Organ Donors: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 34658857
- PMCID: PMC8517172
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.716759
Effects of Terlipressin on Management of Hypotensive Brain-Dead Patients Who are Potential Organ Donors: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
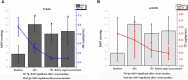
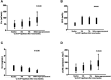
Background: Administration of terlipressin can reverse hypotension in potential organ donors with norepinephrine-resistance. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of terlipressin on the hemodynamics, liver function, and renal function of hypotensive brain-dead patients who were potential organ donors. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted by using the ICU database of one hospital. 18 patients in a total of 294 brain-dead cases were enrolled and administered terlipressin intravenously. All physiological parameters of recruited patients were obtained at baseline, 24 and 72 h after administration, and immediately before organ procurement. Results: Terlipressin induced significant increases in mean arterial pressure (MAP) from 69.56 ± 10.68 mm Hg (baseline) to 101.82 ± 19.27 mm Hg (immediately before organ procurement) and systolic blood pressure (SBP) from 89.78 ± 8.53 mm Hg (baseline) to 133.42 ± 26.11 mm Hg (immediately before organ procurement) in all patients. The increases in MAP were accompanied by significant decreases in heart rate (HR) from 113.56 ± 28.43 bpm (baseline) to 83.89 ± 11.70 bpm (immediately before organ procurement), which resulted in the decrease of norepinephrine dose over time from 0.8 ± 0.2 μg/kg/min (baseline) to 0.09 ± 0.02 μg/kg/min (immediately before organ procurement). There were no changes in central venous pressure, liver function including aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and bilirubin. Renal function, assessed by serum creatinine (SCr), urine output (UOP), creatinine clearance rate (CCr), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), improved significantly. Conclusion: Our analysis of brain-dead patients with hypotension indicates that administration of terlipressin can significantly increases MAP, SBP, UOP, CCr, and eGFR, while decreases HR and Scr. Terlipressin appears to help maintain hemodynamic stability, reduce vasoactive support, and improve renal function.
Keywords: brain-dead; hypotension; mean arterial pressure; organ transplantation; terlipressin.
Copyright © 2021 Zheng, Liu, Chen, Xie, Sun, Wang and Tai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
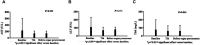
Similar articles
-
Terlipressin in catecholamine-resistant septic shock patients.Shock. 2004 Oct;22(4):314-9. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000136097.42048.bd. Shock. 2004. PMID: 15377885 Clinical Trial.
-
[Comparison of effect of norepinephrine and terlipressin on patients with ARDS combined with septic shock: a prospective single-blind randomized controlled trial].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Feb;29(2):111-116. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.02.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 28625256 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effect of perioperative terlipressin infusion on systemic, hepatic, and renal hemodynamics during living donor liver transplantation.J Crit Care. 2013 Oct;28(5):775-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.02.016. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23618777 Clinical Trial.
-
Terlipressin in brain-death donors.Clin Transplant. 2012 Nov-Dec;26(6):E571-5. doi: 10.1111/ctr.12038. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Clin Transplant. 2012. PMID: 23121213 Review.
-
Effect of Perioperative Terlipressin on Postoperative Renal Function in Patients Who Have Undergone Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Transplant Proc. 2015 Jul-Aug;47(6):1917-25. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.06.023. Transplant Proc. 2015. PMID: 26293074 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

