MicroRNA-195-5p Downregulation Inhibits Endothelial Mesenchymal Transition and Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Targeting Smad7 and Inhibiting Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1-Smads-Snail Pathway
- PMID: 34658906
- PMCID: PMC8514870
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.709123
MicroRNA-195-5p Downregulation Inhibits Endothelial Mesenchymal Transition and Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Targeting Smad7 and Inhibiting Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1-Smads-Snail Pathway
Abstract
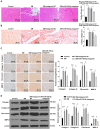
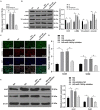
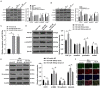
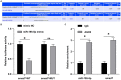
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a complication of diabetes mellitus, which is associated with fibrosis and microRNAs (miRs). This study estimated the mechanism of miR-195-5p in endothelial mesenchymal transition (EndMT) and myocardial fibrosis in DCM. After the establishment of DCM rat models, miR-195-5p was silenced by miR-195-5p antagomir. The cardiac function-related indexes diastolic left ventricular anterior wall (LVAW, d), systolic LVAW (d), diastolic left ventricular posterior wall (LVPW, d), systolic LVPW (d), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and fractional shortening (FS) were measured and miR-195-5p expression in myocardial tissue was detected. Myocardial fibrosis, collagen deposition, and levels of fibrosis markers were detected. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were exposed to high glucose (HG) and miR-195-5p was silenced. The levels of fibrosis proteins, endothelial markers, fibrosis markers, EndMT markers, and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1)/Smads pathway-related proteins were measured in HUVECs. The interaction between miR-195-5p and Smad7 was verified. In vivo, miR-195-5p was highly expressed in the myocardium of DCM rats. Diastolic and systolic LVAW, diastolic and systolic LVPW were increased and LVEF and FS were decreased. Inhibition of miR-195-5p reduced cardiac dysfunction, myocardial fibrosis, collagen deposition, and EndMT, promoted CD31 and VE-cadehrin expressions, and inhibited α-SMA and vimentin expressions. In vitro, HG-induced high expression of miR-195-5p and the expression changes of endothelial markers CD31, VE-cadehrin and fibrosis markers α-SMA and vimentin were consistent with those in vivo after silencing miR-195-5p. In mechanism, miR-195-5p downregulation blocked EndMT by inhibiting TGF-β1-smads pathway. Smad7 was the direct target of miR-195-5p and silencing miR-195-5p inhibited EndMT by promoting Smad7 expression. Collectively, silencing miR-195-5p inhibits TGF-β1-smads-snail pathway by targeting Smad7, thus inhibiting EndMT and alleviating myocardial fibrosis in DCM.
Keywords: TGF-β1-smads-snail pathway; diabetic cardiomyopathy; endothelial mesenchymal transition; miR-195-5p; myocardial fibrosis; smad7.
Copyright © 2021 Ding, Yao, Xie, Wang, Chen, Wei, Ji and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

