Social and Emotional Learning in the Ibero-American Context: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 34659053
- PMCID: PMC8516388
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.738501
Social and Emotional Learning in the Ibero-American Context: A Systematic Review
Abstract
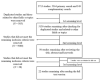
Social and emotional learning (SEL) has acquired great prominence in recent years, due to the skills it develops in students, influencing personal and social well-being. At the same time, society is moving toward a model in which understanding oneself and others is a fundamental aspect in order to function properly on a social level. Studies on SEL programmes have been carried out in various parts of the world, although recent reviews have focused exclusively on the Anglo-Saxon context. Therefore, the aim of this paper was to synthesize research on the efficacy and effectiveness of SEL programmes in Ibero-American contexts in early childhood, primary and secondary education. Systematic review was used as the method of enquiry, following the standards of The Campbell Collaboration. In total, 22 empirical studies of SEL programmes implemented in Ibero-America were collected. The results showed that the SEL variables with the highest incidence and significant results were self-awareness, social awareness, self-control, relationship skills, decision-making, school climate, well-being, and academic achievement. While no studies focused on sense of belonging or school safety. Finally, the establishment of programme components, duration, and integration, for each variable, scientifically evidences the keys that can ensure the success of future SEL programmes.
Keywords: primary education; program assessment; secondary education; social and emotional learning (SEL); socioemotional competences.
Copyright © 2021 Fernández-Martín, Romero-Rodríguez, Marín-Marín and Gómez-García.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilar P., López-Cobo I., Cuadrado F., Benítez I. (2019). Social and emotional competences in Spain: a comparative evaluation between Spanish needs and an international framework based on the experiences of researchers, teachers, and policymakers. Front. Psychol. 10:2127. 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02127 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger C., Milicic N., Alcalay L., Torretti A. (2014). Programa para el Bienestar y Aprendizaje Socioemocional en estudiantes de tercero y cuarto grado: descripción y evaluación de impacto. Rev. Latinoam. Psicol. 46, 169–177. 10.1016/S0120-0534(14)70020-2 - DOI
-
- Campbell D. T., Stanley J. C. (1963). Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs for Research. Evanston, IL: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources