A Novel TLR4-Binding Domain of Peroxiredoxin From Entamoeba histolytica Triggers NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages
- PMID: 34659265
- PMCID: PMC8515043
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.758451
A Novel TLR4-Binding Domain of Peroxiredoxin From Entamoeba histolytica Triggers NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages
Abstract
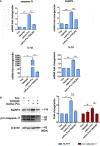
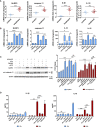
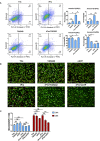
Macrophages promote early host responses to infection by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, and they are crucial to combat amoebiasis, a disease affecting millions of people worldwide. Macrophages elicit pro-inflammatory responses following direct cell/cell interaction of Entamoeba histolytica, inducing NLRP3 inflammasome activation with high-output IL-1β/IL-18 secretion. Here, we found that trophozoites could upregulate peroxiredoxins (Prx) expression and abundantly secrete Prxs when encountering host cells. The C-terminal of Prx was identified as the key functional domain in promoting NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and a recombinant C-terminal domain could act directly on macrophage. The Prxs derived from E. histolytica triggered toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in a cell/cell contact-independent manner. Through genetic, immunoblotting or pharmacological inhibition methods, NLRP3 inflammasome activation was induced through caspase-1-dependent canonical pathway. Our data suggest that E. histolytica Prxs had stable and durable cell/cell contact-independent effects on macrophages following abundantly secretion during invasion, and the C-terminal of Prx was responsible for activating NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. This new alternative pathway may represent a potential novel therapeutic approach for amoebiasis, a global threat to millions.
Keywords: Entamoeba histolytica; NLRP3 inflammasome; TLR4-binding domain; macrophage; peroxiredoxin.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Feng, Zhao, Zhang, Zhou, Zhou, Pang, Tachibana and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The NLRP3 Inflammasome Is a Pathogen Sensor for Invasive Entamoeba histolytica via Activation of α5β1 Integrin at the Macrophage-Amebae Intercellular Junction.PLoS Pathog. 2015 May 8;11(5):e1004887. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004887. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25955828 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-dsDNA antibodies bind to TLR4 and activate NLRP3 inflammasome in lupus monocytes/macrophages.J Transl Med. 2016 Jun 1;14(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0911-z. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27250627 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy Activated by Peroxiredoxin of Entamoeba histolytica.Cells. 2020 Nov 12;9(11):2462. doi: 10.3390/cells9112462. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33198056 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Use of Medicinal Plants and Their Bioactive Derivatives as Alveolar NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulators during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 31;22(17):9497. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179497. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between NLRP3 inflammasome and glycolysis in macrophages: New insights into chronic inflammation pathogenesis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022 Mar;10(3):e581. doi: 10.1002/iid3.581. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022. PMID: 34904398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Functions of Hypoxia in Host-Parasite Interactions: A Focus on Enteric, Tissue, and Blood Protozoa.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 16;11(6):1598. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061598. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37375100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Metabolic Reprogramming in Host Cells Induced by Trophozoites and Intermediate Subunit of Gal/GalNAc Lectins from Entamoeba histolytica.mSystems. 2022 Apr 26;7(2):e0135321. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01353-21. Epub 2022 Mar 28. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 35343800 Free PMC article.
-
Entamoeba histolytica extracellular vesicles drive pro-inflammatory monocyte signaling.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Apr 10;19(4):e0012997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012997. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40208874 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation during parasitic infection.Biosci Rep. 2024 May 29;44(5):BSR20231918. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231918. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38623843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota Crosstalk with Resident Macrophages and Their Role in Invasive Amebic Colitis and Giardiasis-Review.Microorganisms. 2023 May 4;11(5):1203. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051203. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317178 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

