The Effect of miR-520b on Macrophage Polarization and T Cell Immunity by Targeting PTEN in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 34659411
- PMCID: PMC8514911
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5170496
The Effect of miR-520b on Macrophage Polarization and T Cell Immunity by Targeting PTEN in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women. miR-520b had binding sites with PTEN through the bioinformatics prediction. But few studies have been conducted on miR-520b and PTEN in breast cancer. We aimed to explore the effect of miR-520b and PTEN on breast cancer and the mechanisms involved.
Methods: Clinical samples of breast cancer were collected. Bioinformatics analysis was performed to screen the differentially expressed miRNAs. CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells were cocultured with MCF-7 cells in the Transwell system. Moreover, MCF-7 cells and M0 macrophage cocultured cell lines were constructed. qRT-PCR, IF, western blot, flow cytometry, and ELISA were performed to detect related factors expression. Starbase and dual-luciferase reporter assay verified the binding of miR-520b to PTEN. The tumor formation model was established to study miR-520b and PTEN effects in vivo.
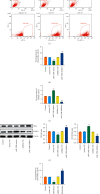
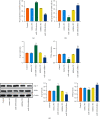
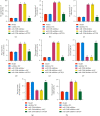
Results: The differentially expressed miR-520b was screened via miRNAs sequencing and cell verification. miR-520b expression was high, PTEN was low in tumor tissues, T cells and NK cells were inhibited, and macrophages were transformed into M2 type, promoting immune escape. In addition, miR-520b bound to PTEN. Then, splenic CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells were successfully sorted. During CD4 T cell differentiation to Th1 and Treg, Th1 was inhibited, and Treg was activated. We found the polarization of macrophages was related to breast cancer. The proportion of CD206 cells increased and CD68 cells decreased in the miR-520b mimics group compared with the mimic NC group. Compared with the inhibitor NC group, the proportion of CD206 cells decreased, and CD68 cells increased in the miR-520b inhibitor group. In vivo experiments showed that miR-520b inhibitor inhibited tumor growth and promoted PTEN expression. The proportion of CD3, CD4, CD8, NK1.1, CD4+IFNγ, and CD68 cells increased, while FOXP3 and CD206 cells decreased in the miR-520b inhibitor group compared with the inhibitor NC group. However, the proportion of CD3, CD4, CD8, NK1.1, CD4+IFNγ, and CD68 cells decreased, while FOXP3 and CD206 cells increased after the addition of siPTEN.
Conclusions: miR-520b inhibited PTEN and aggravated breast tumors. miR-520b inhibitor enhanced CD4 and CD8 cell populations in the tumor immune microenvironment and inhibited tumor growth.
Copyright © 2021 Qin Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of miR-92a-3p/PTEN axis in regulation of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Mar 28;45(3):280-289. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2020.180459. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32386020 Chinese, English.
-
MiR-520b restrains cell growth by targeting HDAC4 in lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Oct;9(10):1249-1254. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12825. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30106218 Free PMC article.
-
miR-520b Promotes Breast Cancer Stemness Through Hippo/YAP Signaling Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 31;12:11691-11700. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S236607. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 32021247 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miR-520b in non-small cell lung cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Nov;16(5):3987-3995. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6732. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30402147 Free PMC article.
-
An Exploration of Oral-Gut Pathogens Mediating Immune Escape of Pancreatic Cancer via miR-21/PTEN Axis.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 22;13:928846. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.928846. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35814712 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction and Bioinformatics Analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network in Acute Myocardial Infarction.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 29;13:854993. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.854993. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35422846 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-transmitted S100A4 induces immunosuppression and non-small cell lung cancer development by activating STAT3.Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 Dec 31;210(3):309-320. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac102. Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36370151 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNA in tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells formation and associated immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 21;14:1228331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1228331. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37671150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Changes after Medical Suppression of Suspected Endometriosis for Implantation Failure: Preliminary Results.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 22;25(13):6852. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136852. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38999962 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Breast cancer tumor microenvironment affects Treg/IL-17-producing Treg/Th17 cell axis: Molecular and therapeutic perspectives.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023 Jan 11;28:132-157. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.01.001. eCollection 2023 Mar 16. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023. PMID: 36816749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

