CMPK2 accelerates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via the NLRP3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 34659504
- PMCID: PMC8515557
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10793
CMPK2 accelerates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via the NLRP3 signaling pathway
Abstract
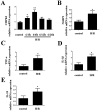
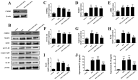
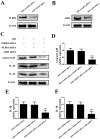
Cytidine monophosphate kinase 2 (CMPK2) is a mitochondrial nucleotide monophosphate kinase which is important for the substrates of mitochondrial DNA synthesis and has been reported to participate in macrophage activation and the inflammatory response. The purpose of the present research was to determine the potential role of CMPK2 in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. The present study investigated the role of CMPK2 in regulating the NLRP3 pathway and liver dysfunction induced by hepatic I/R both in vivo and in vitro. It was revealed that hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) treatment enhanced the mRNA expression levels of CMPK2, NLRP3, IL-18, IL-1β and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells. The protein expression levels of IL-18, IL-1β and cleaved-caspase-1 were decreased following CMPK2 knockdown. Furthermore, the inhibition of AIM2 downregulated the expression level of IL-1β, IL-18 and cleaved-caspase-1 in the CMPK2 knockdown group followed by H/R treatment, while the inhibition of NLRP3 did not. CMPK2 deficiency also decreased alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase expression in mice serum, as well as the pathological changes in the liver. Similarly, the release of IL-18 and IL-1β in mouse serum was also restrained with the decline of CMPK2. In conclusion, the results of the present study demonstrate that CMPK2 is indispensable for NLRP3 inflammasome activation, making CMPK2 an effective target to relieve the liver from I/R injury. In addition, the function of CMPK2 is closely associated with NLRP3 inflammasome activation, instead of AIM2.
Keywords: AIM2; CMPK2; NLRP3 inflammasome; hepatic I/R injury; inflammation.
Copyright: © Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
