Differentially expressed TUG1 and miR-145-5p indicate different severity of chronic heart failure and predict 2-year survival prognosis
- PMID: 34659508
- PMCID: PMC8515550
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10796
Differentially expressed TUG1 and miR-145-5p indicate different severity of chronic heart failure and predict 2-year survival prognosis
Abstract
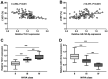
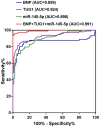
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRs) have critical roles in the progression of various diseases. The present study aimed to investigate the levels and clinical significance of lncRNA taurine upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) and miR-145-5p in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) and explore their indicative value regarding disease severity. TUG1 and miR-145-5p levels were detected by reverse-transcription quantitative PCR. Correlations were examined using Pearson's correlation analysis. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic value of TUG1, miR-145-5p and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP). Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan-Meier method. Cox regression analysis was used to evaluate the prognostic value of TUG1 and miR-145-5p. The levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in serum were detected by ELISA. The results indicated that TUG1 was upregulated and miR-145-5p was downregulated in patients with CHF and they were negatively correlated. TUG1 and miR-145-5p were associated with the left ventricle ejection fraction and were able to indicate the severity of CHF. Serum TUG1 and miR-145-5p had a certain diagnostic value and the combination of BNP, TUG1 and miR-145-5p had high diagnostic accuracy. TUG1 and miR-145-5p were closely associated with overall survival and may function as independent prognostic biomarkers for patients with CHF. In addition, TUG1 and miR-145-5p levels were markedly correlated with inflammation in CHF. Upregulated TUG1 and downregulated miR-145-5p may indicate the severity of CHF, may serve as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and may be involved in CHF progression by regulating inflammatory responses.
Keywords: TUG1; chronic heart failure; diagnosis; inflammation; miR-145-5p; prognosis; severity.
Copyright: © Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Su Q, Zhang P, Yu D, Wu Z, Li D, Shen F, Liao P, Yin G. Upregulation of miR-93 and inhibition of LIMK1 improve ventricular remodeling and alleviate cardiac dysfunction in rats with chronic heart failure by inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway activation. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:7570–7586. doi: 10.18632/aging.102272. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
