Role of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00152 in pancreatic cancer glycolysis via the manipulation of the microRNA-185-5p/Krüppel-like factor 7 axis
- PMID: 34659523
- PMCID: PMC8489139
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.63128
Role of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00152 in pancreatic cancer glycolysis via the manipulation of the microRNA-185-5p/Krüppel-like factor 7 axis
Abstract
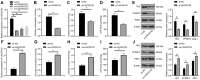
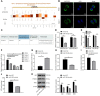
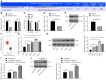
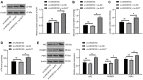
The current study set out to investigate the role of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA (LINC) 00152 in pancreatic cancer (PC) cell glycolysis with the microRNA (miR)-185-5p/Krüppel-like factor 7 (KLF7) axis. Firstly, PC tissues and cells as well as the control ones were collected from 53 PC patients, and assessed for LINC00152 expression patterns. Besides, PC cells with the most differentially expressed LINC00152 were selected for further experiments. When LINC00152 was silenced or overexpressed, PC cell glucose consumption, lactic acid production, adenosine triphosphate and levels of glycolysis-associated enzymes were detected. In addition, the binding relation between LINC00152 and miR-185-5p as well as the target relation between miR-185-5p and KLF7 was clarified and validated. Additionally, xenograft transplantation was performed to confirm the in vitro experiments. It was found that LINC00152 was over-expressed in PC, and it predicted a poor prognosis. Besides, LINC00152 knockdown inhibited PC cell glycolysis. Moreover, LINC00152 could specifically targeted miR-185-5p. Meanwhile, LINC00152 exhaustion blocked PC cell glycolysis through the up-regulation of miR-185-5p. Lastly, LINC00152 inhibition targeted miR-185-5p to quench KLF7, therefore suppressing PC cell tumorigenesis and glycolysis. Collectively, our findings indicated that silencing LINC00152 restricted PC cell glycolysis via promoting miR-185-5p and reducing KLF7.
Keywords: Competing endogenous RNA; Glycolysis; KLF7; Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00152; Pancreatic cancer; Subcellular localization; microRNA-185-5p.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Li S, Xu HX, Wu CT. et al. Angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer: current research status and clinical implications. Angiogenesis. 2019;22:15–36. - PubMed
-
- Goral V. Pancreatic Cancer: Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16:5619–5624. - PubMed
-
- Chu LC, Goggins MG, Fishman EK. Diagnosis and Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer J. 2017;23:333–342. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

