Melatonin effect on platelet count in patients with liver disease
- PMID: 34659664
- PMCID: PMC8514219
Melatonin effect on platelet count in patients with liver disease
Abstract
Aim: A positive effect of melatonin on platelet count in patients with chronic liver disease is reported in the current study.
Background: Thrombocytopenia occurs when the severity of liver disease is exacerbated. Reduction in the secretion of thrombopoetin, as an intrinsic hormone produced mainly by the liver, plays an important role in this complication induced by liver disease.
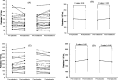
Methods: This research was a double-blind, cross-over, placebo-controlled pilot study. Patients with liver disease were given two 5-mg pearls of melatonin or a placebo for two weeks, and after a 2-week washout period, their groups were switched. Liver function tests and platelet counts were assessed once at the beginning and once at the end of each phase of the study.
Results: In the current study, 40 patients meeting the eligibility criteria were included. The average platelet count was significantly increased by melatonin in comparison with the placebo (from 175.67±92.84 to 191.10±98.82 vs. from 185.22±98.39 to 176.45±91.45) (p-value <0.001). Melatonin also significantly reduced ALT, AST, total bilirubin, and direct and MELD scores in patients with liver disease (p-value <0.05).
Conclusion: Melatonin may increase platelet count and inhibit thrombocytopenia in patients with liver disease; however, more investigations are needed to confirm the current results.
Keywords: Liver disease; Melatonin; Platelet; Thrombopoietic properties.
©2021 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eltrombopag for children with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (PETIT2): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet. 2015 Oct 24;386(10004):1649-58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61107-2. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 26231455 Clinical Trial.
-
A Pilot Randomized, Clinical Trial of the Anti-pruritus Effect of Melatonin in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Spring;20(2):462-472. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.112942.14024. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34567175 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-alpha is effective in the treatment of HIV-1-related, severe, zidovudine-resistant thrombocytopenia. A prospective, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial.Ann Intern Med. 1994 Sep 15;121(6):423-9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-121-6-199409150-00005. Ann Intern Med. 1994. PMID: 8053616 Clinical Trial.
-
Eltrombopag for the treatment of children with persistent and chronic immune thrombocytopenia (PETIT): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled study.Lancet Haematol. 2015 Aug;2(8):e315-25. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00114-3. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Lancet Haematol. 2015. PMID: 26688484 Clinical Trial.
-
Eltrombopag for advanced myelodysplastic syndromes or acute myeloid leukaemia and severe thrombocytopenia (ASPIRE): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial.Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jan;5(1):e34-e43. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30228-4. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Lancet Haematol. 2018. PMID: 29241762 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The Potential of Integrative Cancer Treatment Using Melatonin and the Challenge of Heterogeneity in Population-Based Studies: A Case Report of Colon Cancer and a Literature Review.Curr Oncol. 2024 Apr 3;31(4):1994-2023. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31040149. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38668052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application and investigation of thrombopoiesis-stimulating agents in the treatment of thrombocytopenia.Ther Adv Hematol. 2023 Feb 27;14:20406207231152746. doi: 10.1177/20406207231152746. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Hematol. 2023. PMID: 36865986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afdhal N, McHutchison J, Brown R, Jacobson I, Manns M, Poordad F, et al. Thrombocytopenia associated with chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2008;48:1000–7. - PubMed
-
- Giannini E. Thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease and pharmacologic treatment options. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:1055–65. - PubMed
-
- Bashour FN, Teran JC, Mullen KD. Prevalence of peripheral blood cytopenias (hypersplenism) in patients with nonalcoholic chronic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:2936–9. - PubMed
-
- Pradella P, Bonetto S, Turchetto S, Uxa L, Comar C, Zorat F, et al. Platelet production and destruction in liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2011;54:894–900. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
