Borinostats: solid-phase synthesis of carborane-capped histone deacetylase inhibitors with a tailor-made selectivity profile
- PMID: 34659728
- PMCID: PMC8442681
- DOI: 10.1039/d1sc02268g
Borinostats: solid-phase synthesis of carborane-capped histone deacetylase inhibitors with a tailor-made selectivity profile
Abstract
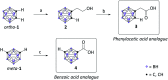
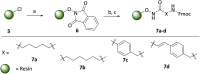
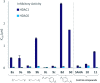
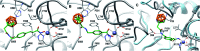
The elevated expression of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in various tumor types renders their inhibition an attractive strategy for epigenetic therapeutics. One key issue in the development of improved HDAC inhibitors (HDACis) is the selectivity for single HDAC isoforms over unspecific pan inhibition to minimize off-target toxicity. Utilizing the carborane moiety as a fine-tuning pharmacophore, we herein present a robust solid phase synthetic approach towards tailor-made HDACis meeting both ends of the selectivity spectrum, namely pan inhibition and highly selective HDAC6 inhibition.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


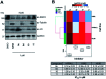
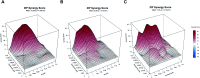
References
-
- Grunstein M. Nature. 1997;389:349–352. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

