tRNA Metabolism and Lung Cancer: Beyond Translation
- PMID: 34660690
- PMCID: PMC8516113
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.659388
tRNA Metabolism and Lung Cancer: Beyond Translation
Abstract
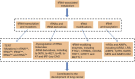
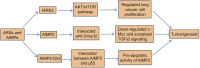
Lung cancer, one of the most malignant tumors, has extremely high morbidity and mortality, posing a serious threat to global health. It is an urgent need to fully understand the pathogenesis of lung cancer and provide new ideas for its treatment. Interestingly, accumulating evidence has identified that transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and tRNA metabolism-associated enzymes not only participate in the protein translation but also play an important role in the occurrence and development of lung cancer. In this review, we summarize the different aspects of tRNA metabolism in lung cancer, such as tRNA transcription and mutation, tRNA molecules and derivatives, tRNA-modifying enzymes, and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARSs), aiming at a better understanding of the pathogenesis of lung cancer and providing new therapeutic strategies for it.
Keywords: lung cancer; pathogenesis; tRNA aminoacylation; tRNA derivatives; tRNA modifications; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2021 Bian, Huang, Yu and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Coll-SanMartin L., Davalos V., Piñeyro D., Rosselló-Tortella M., Bueno-Costa A., Setien F., et al. (2021). Gene Amplification-Associated Overexpression of the Selenoprotein tRNA Enzyme TRIT1 Confers Sensitivity to Arsenic Trioxide in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 13 (8), 1869. 10.3390/cancers13081869 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

