Variability of Retinal Oxygen Metrics in Healthy and Diabetic Subjects
- PMID: 34661625
- PMCID: PMC8525846
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.10.12.20
Variability of Retinal Oxygen Metrics in Healthy and Diabetic Subjects
Abstract
Purpose: Previous studies have reported alterations in total retinal blood flow (TRBF), oxygen delivery (DO2), oxygen metabolism (MO2), and oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) due to retinal diseases. The purposes of the current study were to determine variabilities and establish normal confidence intervals (CIs) for these metrics.
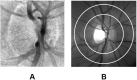
Methods: A total of 22 healthy and 14 diabetic subjects participated in the study. Retinal vascular oxygen saturation (SO2) and TRBF were measured by oximetry and Doppler optical coherence tomography, respectively. DO2, MO2, and OEF were calculated from SO2 and TRBF measurements. Means, standard deviations (SDs), and CIs of metrics were determined in healthy subjects. Intra-visit variability was determined by the mean SDs of repeated measurements. Inter-visit variability was determined by the difference of measurements between two visits.
Results: TRBF was 44 ± 15 µL/min (95% CI, 37-51) in healthy subjects. Intra-visit variabilities of TRBF were 5 µL/min and 6 µL/min in healthy and diabetic subjects, respectively. Inter-visit variability of TRBF was 3 µL/min in diabetic subjects. DO2, MO2, and OEF were 8.3 ± 2.9 µLO2/min (95% CI, 7.0-9.6), 3.2 ± 0.9 µLO2/min (95% CI, 2.8-3.6), and 0.40 ± 0.08 (95% CI, 0.36-0.43), respectively, in healthy subjects. Inter-visit variabilities of DO2, MO2, and OEF were 0.6 µLO2/min, 0.1 µLO2/min, and 0.03, respectively, in diabetic subjects.
Conclusions: The findings established variabilities and normal baselines for TRBF, DO2, MO2, and OEF measurements in a small cohort of subjects.
Translational relevance: The variability and normal baselines of retinal oxygen metrics may be useful for diagnosing and monitoring patients with retinal diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


References
-
- Tayyari F, Khuu LA, Flanagan JG, Singer S, Brent MH, Hudson C.. Retinal blood flow and retinal blood oxygen saturation in mild to moderate diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015; 56: 6796–6800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

