Phase II multicentre, double-blind, randomised trial of ustekinumab in adolescents with new-onset type 1 diabetes (USTEK1D): trial protocol
- PMID: 34663658
- PMCID: PMC8524290
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049595
Phase II multicentre, double-blind, randomised trial of ustekinumab in adolescents with new-onset type 1 diabetes (USTEK1D): trial protocol
Abstract
Introduction: Most individuals newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (T1D) have 10%-20% of beta-cell function remaining at the time of diagnosis. Preservation of residual beta-cell function at diagnosis may improve glycaemic control and reduce longer-term complications.Immunotherapy has the potential to preserve endogenous beta-cell function and thereby improve metabolic control even in poorly compliant individuals. We propose to test ustekinumab (STELARA), a targeted and well-tolerated therapy that may halt T-cell and cytokine-mediated destruction of beta-cells in the pancreas at the time of diagnosis.
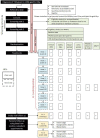
Methods and analysis: This is a double-blind phase II study to assess the safety and efficacy of ustekinumab in 72 children and adolescents aged 12-18 with new-onset T1D.Participants should have evidence of residual functioning beta-cells (serum C-peptide level >0.2nmol/L in the mixed-meal tolerance test (MMTT) and be positive for at least one islet autoantibody (GAD, IA-2, ZnT8) to be eligible.Participants will be given ustekinumab/placebo subcutaneously at weeks 0, 4 and 12, 20, 28, 36 and 44 in a dose depending on the body weight and will be followed for 12 months after dose 1.MMTTs will be used to measure the efficacy of ustekinumab for preserving C-peptide area under the curve at week 52 compared with placebo. Secondary objectives include further investigations into the efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, patient and parent questionnaires, alternative methods for measuring insulin production and exploratory mechanistic work.
Ethics and dissemination: This trial received research ethics approval from the Wales Research Ethics Committee 3 in September 2018 and began recruiting in December 2018.The results will be disseminated using highly accessed, peer-reviewed medical journals and presented at conferences.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN14274380.
Keywords: diabetes & endocrinology; paediatric endocrinology; statistics & research methods.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Wood JR, Miller KM, Maahs DM, et al. . Most youth with type 1 diabetes in the T1D exchange clinic registry do not meet American diabetes association or International Society for pediatric and adolescent diabetes clinical guidelines. Diabetes Care 2013;36:2035–7. 10.2337/dc12-1959 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Diabetes death rates among youths aged ≤ 19 years--United States, 1968-2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2012;61:869–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical