Distinction of lymphoid and myeloid clonal hematopoiesis
- PMID: 34663986
- PMCID: PMC8621497
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01521-4
Distinction of lymphoid and myeloid clonal hematopoiesis
Abstract
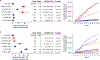
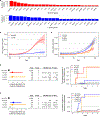
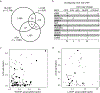
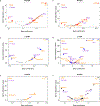
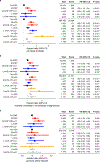
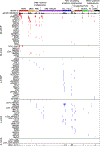
Clonal hematopoiesis (CH) results from somatic genomic alterations that drive clonal expansion of blood cells. Somatic gene mutations associated with hematologic malignancies detected in hematopoietic cells of healthy individuals, referred to as CH of indeterminate potential (CHIP), have been associated with myeloid malignancies, while mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCAs) have been associated with lymphoid malignancies. Here, we analyzed CHIP in 55,383 individuals and autosomal mCAs in 420,969 individuals with no history of hematologic malignancies in the UK Biobank and Mass General Brigham Biobank. We distinguished myeloid and lymphoid somatic gene mutations, as well as myeloid and lymphoid mCAs, and found both to be associated with risk of lineage-specific hematologic malignancies. Further, we performed an integrated analysis of somatic alterations with peripheral blood count parameters to stratify the risk of incident myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. These genetic alterations can be readily detected in clinical sequencing panels and used with blood count parameters to identify individuals at high risk of developing hematologic malignancies.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
BLE has received research funding from Celgene, Deerfield, and Novartis and consulting fees from GRAIL. He serves on the scientific advisory boards for Skyhawk Therapeutics, Exo Therapeutics, and Neomorph Therapeutics, none of which are directly related to the content of this paper. PN reports grant support from Amgen, Apple, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Novartis, personal fees from Apple, AstraZeneca, Blackstone Life Sciences, Genentech, and Novartis, and spousal employment at Vertex, all unrelated to the present work. GKG reports affiliation to Moderna Therapeutics which is unrelated to the present work. MA received consulting fees from German Accelerator Life Sciences and he is co-founder of iuvando Health and holds equity, all unrelated to the present work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


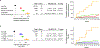



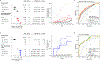
References
Methods References
-
- Benjamin D, et al. Calling somatic SNVs and indels with Mutect2. bioRxiv (2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- T32 HL094301/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA253125/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151283/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA206963/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 CA066996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA108631/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL148050/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL082945/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148565/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142711/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

