Novel coronavirus pathogen in humans and animals: an overview on its social impact, economic impact, and potential treatments
- PMID: 34664166
- PMCID: PMC8523003
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-16809-8
Novel coronavirus pathogen in humans and animals: an overview on its social impact, economic impact, and potential treatments
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Novel coronavirus pathogen in humans and animals: an overview on its social impact, economic impact, and potential treatments.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Mar;29(12):18309. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-18766-2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35044613 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
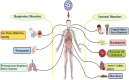
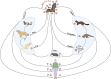
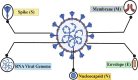
In the light of thousands of infections and deaths, the World Health Organization (WHO) has declared the outbreak of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) a worldwide pandemic. It has spread to about 22 million people worldwide, with a total of 0.45 million expiries, limiting the movement of most people worldwide in the last 6 months. However, COVID-19 became the foremost health, economic, and humanitarian challenge of the twenty-first century. Measures intended to curb the pandemic of COVID-19 included travel bans, lockdowns, and social distances through shelter orders, which will further stop human activities suddenly and eventually impact the world and the national economy. The viral disease is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). After SARS-CoV-2 virus and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-related CoV, COVID-19 is the third most significant lethal disease to humans. According to WHO, COVID-19 mortality exceeded that of SARS and MERS since COVID-19 was declared an international public health emergency. Genetic sequencing has recently established that COVID-19 is close to SARS-CoV and bat coronavirus which has not yet been recognized as the key cause of this pandemic outbreak, its transmission, and human pathogen mechanism. This review focuses on a brief introduction of novel coronavirus pathogens, including coronavirus in humans and animals, its taxonomic classification, symptoms, pathogenicity, social impact, economic impact, and potential treatment therapy for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Economy; Emerging pathogens; Novel coronavirus; Potential treatment; Social impact.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Agostini ML, Andres EL, Sims AC, Graham RL, Sheahan TP, Lu X, Smith EC, Case JB, Feng JY, Jordan R, Ray AS, Cihlar T, Siegel D, Mackman RL, Clarke MO, Baric RS, Denison MR, Jordan RJM (2018) Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. 9(2) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Approved vaccine (2021) https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-00502-w. Accesed 1 Aug 2021
-
- Arabi YM, Deeb AM, Al-Hameed F, Mandourah Y, Almekhlafi GA, Sindi AA, Al-Omari A, Shalhoub S, Mady A, Alraddadi B, Almotairi A, Al Khatib K, Abdulmomen A, Qushmaq I, Solaiman O, Al-Aithan AM, Al-Raddadi R, Ragab A, Al Harthy A, Kharaba A, Jose J, Dabbagh T, Fowler RA, Balkhy HH, Merson L, Hayden FG; Saudi Critical Care Trials group (2019) Macrolides in critically ill patients with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome. 81, 184–190 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

