Current treatment strategies for COVID‑19 (Review)
- PMID: 34664677
- PMCID: PMC8548951
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12498
Current treatment strategies for COVID‑19 (Review)
Abstract
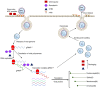
The spread of the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) emerged suddenly at the end of 2019 and the disease came to be known as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19). To date, there is no specific therapy established to treat COVID‑19. Identifying effective treatments is urgently required to treat patients and stop the transmission of SARS‑CoV‑2 in humans. For the present review, >100 publications on therapeutic agents for COVID‑19, including in vitro and in vivo animal studies, case reports, retrospective analyses and meta‑analyses were retrieved from PubMed and analyzed, and promising therapeutic agents that may be used to combat SARS‑CoV‑2 infection were highlighted. Since the outbreak of COVID‑19, different drugs have been repurposed for its treatment. Existing drugs, including chloroquine (CQ), its derivative hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), remdesivir and nucleoside analogues, monoclonal antibodies, convalescent plasma, Chinese herbal medicine and natural compounds for treating COVID‑19 evaluated in experimental and clinical studies were discussed. Although early clinical studies suggested that CQ/HCQ produces antiviral action, later research indicated certain controversy regarding their use for treating COVID‑19. The molecular mechanisms of these therapeutic agents against SARS‑CoV2 have been investigated, including inhibition of viral interactions with angiotensin‑converting enzyme 2 receptors in human cells, viral RNA‑dependent RNA polymerase, RNA replication and the packaging of viral particles. Potent therapeutic options were reviewed and future challenges to accelerate the development of novel therapeutic agents to treat and prevent COVID‑19 were acknowledged.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; RNA‑dependent RNA polymerase; antibodies; coronavirus disease 2019; nucleoside analogues; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kuhn JH, Radoshitzky SR, Li W, Wong SK, Choe H, Farzan M. The SARS Coronavirus receptor ACE 2 A potential target for antiviral therapy. In: Holzenburg A, Bogner E, editors. New Concepts of Antiviral Therapy. Springer US; Boston, MA: 2006. pp. 397–418. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

