Oral and gastric microbiome in relation to gastric intestinal metaplasia
- PMID: 34664721
- PMCID: PMC8770574
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.33848
Oral and gastric microbiome in relation to gastric intestinal metaplasia
Abstract
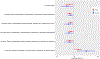
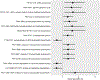
Evidence suggests that Helicobacter pylori plays a role in gastric cancer (GC) initiation. However, epidemiologic studies on the specific role of other bacteria in the development of GC are lacking. We conducted a case-control study of 89 cases with gastric intestinal metaplasia (IM) and 89 matched controls who underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy at three sites affiliated with NYU Langone Health. We performed shotgun metagenomic sequencing using oral wash samples from 89 case-control pairs and antral mucosal brushing samples from 55 case-control pairs. We examined the associations of relative abundances of bacterial taxa and functional pathways with IM using conditional logistic regression with and without elastic-net penalty. Compared with controls, oral species Peptostreptococcus stomatis, Johnsonella ignava, Neisseria elongata and Neisseria flavescens were enriched in cases (odds ratios [ORs] = 1.29-1.50, P = .004-.01) while Lactobacillus gasseri, Streptococcus mutans, S parasanguinis and S sanguinis were under-represented (ORs = 0.66-0.76, P = .006-.042) in cases. Species J ignava and Filifactor alocis in the gastric microbiota were enriched (ORs = 3.27 and 1.43, P = .005 and .035, respectively), while S mutans, S parasanguinis and S sanguinis were under-represented (ORs = 0.61-0.75, P = .024-.046), in cases compared with controls. The lipopolysaccharide and ubiquinol biosynthesis pathways were more abundant in IM, while the sugar degradation pathways were under-represented in IM. The findings suggest potential roles of certain oral and gastric microbiota, which are correlated with regulation of pathways associated with inflammation, in the development of gastric precancerous lesions.
Keywords: case-control study; gastric intestinal metaplasia; gastric microbiome; oral microbiome; shotgun metagenomic sequencing.
© 2021 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021. - PubMed
-
- Correa P. Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process--First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Res 1992;52:6735–40. - PubMed
-
- Ernst PB, Peura DA, Crowe SE. The translation of Helicobacter pylori basic research to patient care. Gastroenterology 2006;130:188–206; quiz 12–3. - PubMed
-
- Kwak HW, Choi IJ, Cho SJ, et al. Characteristics of gastric cancer according to Helicobacter pylori infection status. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;29:1671–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

