Clinical outcomes of all-ceramic single crowns and fixed dental prostheses supported by ceramic implants: A systematic review and meta-analyses
- PMID: 34665900
- PMCID: PMC9297865
- DOI: 10.1111/clr.13871
Clinical outcomes of all-ceramic single crowns and fixed dental prostheses supported by ceramic implants: A systematic review and meta-analyses
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the clinical outcomes of all-ceramic single crowns (SCs) and fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) supported by ceramic implants.
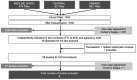
Materials and methods: Based on a focused question and customized PICO framework, electronic (Medline/EMBASE/Cochrane) and manual searches for studies reporting the clinical outcomes of all-ceramic SCs and FDPs supported by ceramic implants ≥12 months were performed. The primary outcomes were reconstruction survival and the chipping proportion. The secondary outcomes were implant survival, technical complications, and patient-related outcome measurements. Meta-analyses were performed after 1, 2, and 5 years using random-effect meta-analyses.
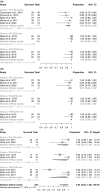
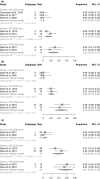
Results: Eight of the 1,403 initially screened titles and 55 full texts were included. Five reported on monolithic lithium disilicate (LS2) SCs, one on veneered zirconia SCs, and two on veneered zirconia SCs and FDPs, which reported all on cement-retained reconstructions (mean observation: 12.0-61.0 months). Meta-analyses estimated a 5-year survival rate of 94% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 82%-100%) for overall implant survival. Reconstruction survival proportions after 5 years were: monolithic LS2, 100% (95%CI: 95%-100%); veneered zirconia SCs, 89% (95%CI: 62%-100%); and veneered zirconia FDPs 94% (95%CI: 81%-100%). The chipping proportion after 5 years was: monolithic LS2, 2% (95%CI: 0%-11%); veneered zirconia SCs, 38% (95%CI: 24%-54%); and veneered zirconia FDPs, 57% (95%CI: 38%-76%). Further outcomes were summarized descriptively.
Conclusions: Due to the limited data available, only tendencies could be identified. All-ceramic reconstructions supported by ceramic implants demonstrated promising survival rates after mid-term observation. However, high chipping proportions of veneered zirconia SCs and, particularly, FDPs diminished the overall outcome. Monolithic LS2 demonstrated fewer clinical complications. Monolithic reconstructions could be a valid treatment option for ceramic implants.
Keywords: ceramics; dental implants; implant-supported dental prosthesis; meta-analysis; survival analysis; systematic review; treatment outcome; zirconia.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Oral Implants Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest regarding the authorship and/or publication of this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Balmer, M. , Spies, B. C. , Kohal, R. J. , Hämmerle, C. H. , Vach, K. , & Jung, R. E. (2020). Zirconia implants restored with single crowns or fixed dental prostheses: 5‐year results of a prospective cohort investigation. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 31(5), 452–462. 10.1111/clr.13581 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Becker, J. , John, G. , Becker, K. , Mainusch, S. , Diedrichs, G. , & Schwarz, F. (2017). Clinical performance of two‐piece zirconia implants in the posterior mandible and maxilla: A prospective cohort study over 2 years. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 28(1), 29–35. 10.1111/clr.12610 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cannizzaro, G. , Torchio, C. , Felice, P. , Leone, M. , & Esposito, M. (2010). Immediate occlusal versus non‐occlusal loading of single zirconia implants. A multicentre pragmatic randomised clinical trial. European Journal of Oral Implantology, 3(2), 111–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

