Management and outcomes in critically ill nonagenarian versus octogenarian patients
- PMID: 34666709
- PMCID: PMC8524896
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-021-02476-4
Management and outcomes in critically ill nonagenarian versus octogenarian patients
Abstract
Background: Intensive care unit (ICU) patients age 90 years or older represent a growing subgroup and place a huge financial burden on health care resources despite the benefit being unclear. This leads to ethical problems. The present investigation assessed the differences in outcome between nonagenarian and octogenarian ICU patients.
Methods: We included 7900 acutely admitted older critically ill patients from two large, multinational studies. The primary outcome was 30-day-mortality, and the secondary outcome was ICU-mortality. Baseline characteristics consisted of frailty assessed by the Clinical Frailty Scale (CFS), ICU-management, and outcomes were compared between octogenarian (80-89.9 years) and nonagenarian (> 90 years) patients. We used multilevel logistic regression to evaluate differences between octogenarians and nonagenarians.
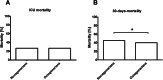
Results: The nonagenarians were 10% of the entire cohort. They experienced a higher percentage of frailty (58% vs 42%; p < 0.001), but lower SOFA scores at admission (6 + 5 vs. 7 + 6; p < 0.001). ICU-management strategies were different. Octogenarians required higher rates of organ support and nonagenarians received higher rates of life-sustaining treatment limitations (40% vs. 33%; p < 0.001). ICU mortality was comparable (27% vs. 27%; p = 0.973) but a higher 30-day-mortality (45% vs. 40%; p = 0.029) was seen in the nonagenarians. After multivariable adjustment nonagenarians had no significantly increased risk for 30-day-mortality (aOR 1.25 (95% CI 0.90-1.74; p = 0.19)).
Conclusion: After adjustment for confounders, nonagenarians demonstrated no higher 30-day mortality than octogenarian patients. In this study, being age 90 years or more is no particular risk factor for an adverse outcome. This should be considered- together with illness severity and pre-existing functional capacity - to effectively guide triage decisions.
Trial registration: NCT03134807 and NCT03370692 .
Keywords: Frailty; Intensive care medicine; Nonagenarians; Octogenarians; Outcome.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.