The impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on rhegmatogenous retinal detachment treatment patterns
- PMID: 34666710
- PMCID: PMC8524212
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-021-02127-7
The impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on rhegmatogenous retinal detachment treatment patterns
Abstract
Backgrounds: To describe changes in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) surgical procedures in Beijing during the COVID-19 Pandemic.
Methods: A retrospective cohort of RRD patients was analyzed. Patients were divided into the COVID-19 pandemic group and pre-COVID-19 group according to their presentation. The presurgery characteristics, surgical procedures, and surgery outcomes were collected. The potential factors related to the choice of pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) or scleral buckling (SB) were analyzed using logistic regression. The differences in the procedure choice under specific conditions were compared. Surgery outcomes were compared between the two groups.
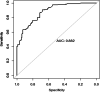
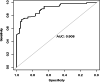
Results: In the COVID-19 pandemic group, less patients received SB (27.8, 41.3%, p = 0.02) while more patients received PPV (72.2, 58.6%, p = 0.02); in patients who received SB, fewer patients received subretinal fluid drainage (45.4,75.7%, p = 0.01); in patients who received PPV, fewer patients received phacovitrectomy (7.0, 21.0%, p = 0.02). The choice of PPV was related to older age (1.03, p = 0.005), the presence of RRD with choroidal detachment (RRD-CD) (2.92, p = 0.03), pseudophakia (5.0, p = 0.002), retinal breaks located posterior to the equator (4.87, p < 0.001), macular holes (9.76, p = 0.005), and a presurgery visual acuity (VA) less than 0.02 (0.44, p = 0.03). Fewer phakia patients with retinal breaks located posterior to the equator (1/28, 11/30, p = 0.01) and fewer patients with chronic RRD and subretinal strand (1/9, 9/16, p = 0.03) received SB in the COVID-19 pandemic group. There were more patients with improved VA (55.7, 40.2%, p = 0.03) in the COVID-19 pandemic group. The overall single-surgery retinal attachment rate was similar in the two groups (94.9, 94.5%, p = 0.99).
Conclusions: During the COVID-19 Pandemic, the main reason for the increased number of PPV in RRD treatment was that more complicated cases were presented. However, the surgeons were conservative in procedure choice in specific cases. The adjustments on RRD treatments lead to comparable surgery outcomes.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment; Surgery.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Borowicz D, Nowomiejska K, Nowakowska D, Brzozowska A, Toro MD, Avitabile T, Jünemann AG, Rejdak R. Functional and morphological results of treatment of macula-on and macula-off rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with pars plana vitrectomy and sulfur hexafluoride gas tamponade. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019;19(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1120-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nishitsuka K, Kawasaki R, Yamakiri K, Baba T, Koto T, Yamashita H, Sakamoto T. Preoperative factors to select vitrectomy or scleral buckling for retinal detachment in microincision vitrectomy era. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020;258(9):1871–1880. doi: 10.1007/s00417-020-04744-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous