Efficacy of occlusive wraps used for delivery room care
- PMID: 34667067
- PMCID: PMC9606500
- DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2021-322611
Efficacy of occlusive wraps used for delivery room care
Abstract
Background: Guidelines advise for more than 20 years to use occlusive plastic wraps for temperature management during delivery room care but data on efficacy of different types of wrap are still scarce.
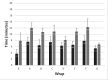
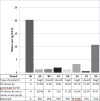
Methods: A random sample of seven different types of plastic wrap was tested using prewarmed aluminium blocks.
Results: The most effective wrap increased the time to cool by 2°C by one-third for the core and by 100% for the surface whereas the least effective wrap led to even faster heat loss compared with no wrap at all. The least effective wrap concerning all capacities tested was made from polyurethane that contains potentially toxic and narcotic monomers. Heat and water retention did not correlate to wrap thickness.
Discussion: Large differences in heat and water retention capacity warrant a careful choice of the type of wrap as some might be counterproductive. Wraps containing polyurethane should not be used.
Keywords: emergency care; intensive care units; neonatal; toxicology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heat loss prevention in the delivery room for preterm infants: a national survey of newborn intensive care units.J Perinatol. 2005 Aug;25(8):514-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211344. J Perinatol. 2005. PMID: 15931234
-
Heat loss prevention for preterm infants in the delivery room.J Perinatol. 2005 May;25(5):304-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211289. J Perinatol. 2005. PMID: 15861196 Clinical Trial.
-
Reducing hypothermia in preterm infants with polyethylene wrap.Pediatr Int. 2011 Aug;53(4):468-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2010.03295.x. Pediatr Int. 2011. PMID: 21105964 Clinical Trial.
-
Maintaining normothermia: Why and how?Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018 Oct;23(5):333-339. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018. PMID: 29599071 Review.
-
Heat loss prevention: a systematic review of occlusive skin wrap for premature neonates.J Perinatol. 2005 Dec;25(12):763-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211392. J Perinatol. 2005. PMID: 16292338
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
