Immunosuppressive metabolites in tumoral immune evasion: redundancies, clinical efforts, and pathways forward
- PMID: 34667078
- PMCID: PMC8527165
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003013
Immunosuppressive metabolites in tumoral immune evasion: redundancies, clinical efforts, and pathways forward
Abstract
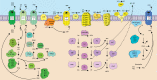
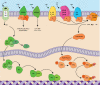
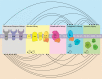
Tumors accumulate metabolites that deactivate infiltrating immune cells and polarize them toward anti-inflammatory phenotypes. We provide a comprehensive review of the complex networks orchestrated by several of the most potent immunosuppressive metabolites, highlighting the impact of adenosine, kynurenines, prostaglandin E2, and norepinephrine and epinephrine, while discussing completed and ongoing clinical efforts to curtail their impact. Retrospective analyses of clinical data have elucidated that their activity is negatively associated with prognosis in diverse cancer indications, though there is a current paucity of approved therapies that disrupt their synthesis or downstream signaling axes. We hypothesize that prior lukewarm results may be attributed to redundancies in each metabolites' synthesis or signaling pathway and highlight routes for how therapeutic development and patient stratification might proceed in the future.
Keywords: adenosine; immunotherapy; indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase; metabolic networks and pathways; tumor escape.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JB has IP related to PEG-KYNase enzymes and has received consulting income from Ikena Oncology. DM has IP interests in the therapeutic use of IDO inhibitors; and has received consulting income and research support from NewLink Genetics/Lumos Pharma. MRJ is supported by a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship. DM receives funding from the NIH (R01CA103320 and R01CA211229). JB receives funding from the Emory University Winship Cancer Center and the Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The potential of targeting indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase for cancer treatment.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015 May;19(5):605-15. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.995092. Epub 2015 Feb 15. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 25684107 Review.
-
IDO1 in cancer: a Gemini of immune checkpoints.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 May;15(5):447-457. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.143. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29375124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the IDO1 pathway in cancer: from bench to bedside.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Aug 2;11(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0644-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30068361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoregulatory signal networks and tumor immune evasion mechanisms: insights into therapeutic targets and agents in clinical development.Biochem J. 2022 Oct 28;479(20):2219-2260. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210233. Biochem J. 2022. PMID: 36305711 Review.
-
[Development of novel immunotherapy targeting cancer immune evasion].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2014 Sep;41(9):1062-5. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2014. PMID: 25248888 Japanese.
Cited by
-
Rational engineering of an improved adenosine deaminase 2 enzyme for weaponizing T-cell therapies.Immunooncol Technol. 2023 Jun 28;19:100394. doi: 10.1016/j.iotech.2023.100394. eCollection 2023 Sep. Immunooncol Technol. 2023. PMID: 37519414 Free PMC article.
-
Fuel for thought: targeting metabolism in lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 31;13(12):3692-3717. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-662. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39830762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Kynurenine/AhR Pathway in Diseases Related to Metabolism and Cancer.Int J Tryptophan Res. 2023 Sep 14;16:11786469231185102. doi: 10.1177/11786469231185102. eCollection 2023. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2023. PMID: 37719171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering CREB-activated promoters for adenosine-induced gene expression.Biotechnol J. 2024 Feb;19(2):e2300446. doi: 10.1002/biot.202300446. Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38403442 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin Potentially Treating Prostate Cancer and COVID-19 Analyzed by the Bioinformatics Approach: Clinical Findings and Drug Targets.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 1;12:802447. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.802447. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35178029 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
