Roles of mechanosensitive channel Piezo1/2 proteins in skeleton and other tissues
- PMID: 34667178
- PMCID: PMC8526690
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-021-00168-8
Roles of mechanosensitive channel Piezo1/2 proteins in skeleton and other tissues
Abstract
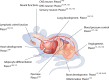
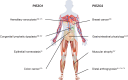
Mechanotransduction is a fundamental ability that allows living organisms to receive and respond to physical signals from both the external and internal environments. The mechanotransduction process requires a range of special proteins termed mechanotransducers to convert mechanical forces into biochemical signals in cells. The Piezo proteins are mechanically activated nonselective cation channels and the largest plasma membrane ion channels reported thus far. The regulation of two family members, Piezo1 and Piezo2, has been reported to have essential functions in mechanosensation and transduction in different organs and tissues. Recently, the predominant contributions of the Piezo family were reported to occur in the skeletal system, especially in bone development and mechano-stimulated bone homeostasis. Here we review current studies focused on the tissue-specific functions of Piezo1 and Piezo2 in various backgrounds with special highlights on their importance in regulating skeletal cell mechanotransduction. In this review, we emphasize the diverse functions of Piezo1 and Piezo2 and related signaling pathways in osteoblast lineage cells and chondrocytes. We also summarize our current understanding of Piezo channel structures and the key findings about PIEZO gene mutations in human diseases.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

