NR4A2 expression is not altered in placentas from cases of growth restriction or preeclampsia, but is reduced in hypoxic cytotrophoblast
- PMID: 34667209
- PMCID: PMC8526588
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-00192-y
NR4A2 expression is not altered in placentas from cases of growth restriction or preeclampsia, but is reduced in hypoxic cytotrophoblast
Abstract
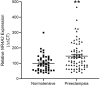
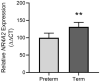
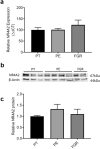
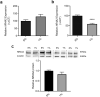
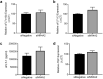
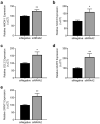
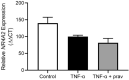
Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 2 (NR4A2) transcripts are elevated in the circulation of individuals whose pregnancies are complicated by preterm fetal growth restriction (FGR). In this paper, we show that the cases with preeclampsia (PE) have increased circulating NR4A2 transcripts compared to those with normotensive FGR. We aimed to establish whether the dysfunctional placenta mirrors the increase in NR4A2 transcripts and further, to uncover the function of placental NR4A2. NR4A2 expression was detected in preterm and term placental tissue; expressed higher at term. NR4A2 mRNA expression and protein were not altered in placentas from preterm FGR or PE pregnancies. Hypoxia (1% O2 compared to 8% O2) significantly reduced cytotrophoblast NR4A2 mRNA expression, but not placental explant NR4A2 expression. Silencing cytotrophoblast NR4A2 expression under hypoxia (via short interfering (si)RNAs) did not alter angiogenic Placental Growth Factor, nor anti-angiogenic sFlt-1 mRNA expression or protein secretion, but increased expression of cellular antioxidant, oxidative stress, inflammatory, and growth genes. NR4A2 expression was also not altered in a model of tumour necrosis factor-α-induced endothelial dysfunction, or with pravastatin treatment. Further studies are required to identify the origin of the circulating transcripts in pathological pregnancies, and investigate the function of placental NR4A2.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LOX-1 expression is reduced in placenta from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia and in hypoxic cytotrophoblast.Pregnancy Hypertens. 2021 Aug;25:255-261. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2021.07.243. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 34325289
-
Phosphoglucomutase 5 gene transcripts are expressed by the human placenta and differentially regulated in placental dysfunction.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 3;15(1):11381. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94498-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40180976 Free PMC article.
-
DAAM2 is elevated in the circulation and placenta in pregnancies complicated by fetal growth restriction and is regulated by hypoxia.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 10;11(1):5540. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84785-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33692394 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adaptations of the human placenta to hypoxia: opportunities for interventions in fetal growth restriction.Hum Reprod Update. 2021 Apr 21;27(3):531-569. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmaa053. Hum Reprod Update. 2021. PMID: 33377492 Review.
-
Is there a role for placental senescence in the genesis of obstetric complications and fetal growth restriction?Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Feb;218(2S):S762-S773. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.11.567. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29275823 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrauterine Growth Restriction: Need to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy and Evidence for a Key Role of Oxidative Stress in Neonatal and Long-Term Sequelae.Cells. 2024 Mar 13;13(6):501. doi: 10.3390/cells13060501. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534344 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

