Giant Meckel's Diverticulitis Perforation Due to Necrosis
- PMID: 34667673
- PMCID: PMC8519317
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.17997
Giant Meckel's Diverticulitis Perforation Due to Necrosis
Abstract
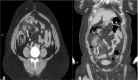
Although Meckel's diverticulum (MD) is the most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract, its prevalence is approximately 2% in the general population. Most diverticula remain asymptomatic and can be diagnosed with obstruction, perforation, inflammation, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage. The treatment of complicated MD is surgery, but there is no clear treatment recommendation yet for incidentally detected cases. As in the case we present here, the development of perforation due to Giant Meckel's diverticulitis in an adult female patient is a very rare complication of a disease that can be diagnosed very rarely.
Keywords: complication; giant; meckel’s diverticulitis; perforation; right-sided abdominal pain.
Copyright © 2021, Dirim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Stallion A, Shuck JM. Surgical Treatment. Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. Munich, Germany: Zuckschwerdt; 2017. Meckel’s diverticulum.
-
- Meckel's diverticulum in the adult. Lequet J, Menahem B, Alves A, Fohlen A, Mulliri A. J Visc Surg. 2017;154:253–259. - PubMed
-
- Meckel's diverticulum: clinical features, diagnosis and management. Kuru S, Kismet K. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2018;110:726–732. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials