Square-root Palatoplasty: Comparing a Novel Modified-Furlow Double-opposing Z-palatoplasty Technique to Traditional Straight-line Repair
- PMID: 34667705
- PMCID: PMC8517311
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003777
Square-root Palatoplasty: Comparing a Novel Modified-Furlow Double-opposing Z-palatoplasty Technique to Traditional Straight-line Repair
Abstract
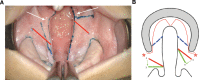
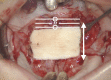
The purpose of this study was to introduce a modification of the Furlow double-opposing Z-plasty (DOZ)-the square-root palatoplasty (SRP)-and critically evaluate outcomes compared to children who underwent straight-line repair (SLR).
Methods: A retrospective review was performed of all nonsyndromic children undergoing primary cleft palate closure either by SRP or SLR at our institution between 2009 and 2017. Outcomes of interest included rates/location of oronasal fistula, secondary surgery, speech delay/deficits, resonance, nasal air emission (NAE), articulation errors, and velopharyngeal function. Logistic regression was used to assess for the effect of surgery type on outcomes while controlling for Veau cleft type, age, and gender.
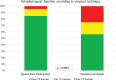
Results: Seventy-eight patients were included; 46 (59%) underwent SRP, and 32 (41%) underwent SLR. The mean follow-up was 4.07 years. When compared to SLR, children who underwent SRP were less likely to have oronasal fistula [odds ratio (OR) 4.8, P = 0.0159], speech delay/deficits (OR 7.7, P < 0.001), NAE (OR 9.7, P < 0.001), articulation errors (OR 10.2, P < 0.001), or need for secondary speech surgery (OR 13.2, P < 0.0002). Patients who underwent SRP were also more likely to have normal resonance (78.26% versus 43.75%, respectively; P = 0.0043) and good VP function (84.78% versus 56.25%, respectively; P = 0.0094).
Conclusions: This study describes and evaluates outcomes following a modified-Furlow DOZ technique-the SRP. After adjusting for Veau classification, age, and gender in nonsyndromic children, SRP is associated with significantly less speech delay/deficits, NAE, articulation errors, and need for secondary speech surgery when compared to children who underwent SLR.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- Furlow LT, Jr. Cleft palate repair by double opposing Z-plasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986;78:724–738. - PubMed
-
- Katzel EB, Basile P, Koltz PF, et al. Current surgical practices in cleft care: cleft palate repair techniques and postoperative care. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:899–906. - PubMed
-
- Pet MA, Marty-Grames L, Blount-Stahl M, et al. The Furlow palatoplasty for velopharyngeal dysfunction: velopharyngeal changes, speech improvements, and where they intersect. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2015;52:12–22. - PubMed
-
- Randall P, LaRossa D, Solomon M, et al. Experience with the Furlow double-reversing Z-plasty for cleft palate repair. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986;77:569–576. - PubMed
-
- Noorchashm N, Dudas JR, Ford M, et al. Conversion Furlow palatoplasty: salvage of speech after straight-line palatoplasty and “incomplete intravelar veloplasty”. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56:505–510. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
