Malnutrition in Biliary Atresia: Assessment, Management, and Outcomes
- PMID: 34669243
- PMCID: PMC8857023
- DOI: 10.1002/lt.26339
Malnutrition in Biliary Atresia: Assessment, Management, and Outcomes
Abstract
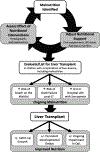
Children with biliary atresia (BA), particularly infants, are at high risk for malnutrition attributed to a multitude of factors, including poor oral intake and intolerance of enteral feeding, fat malabsorption, abnormal nutrient metabolism, and increased caloric demand. Malnutrition and sarcopenia negatively impact outcomes in BA, leading to higher pretransplant and posttransplant morbidity and mortality. This review summarizes factors contributing to nutritional deficiencies in BA and offers an organized approach to the assessment and management of malnutrition in this vulnerable population.
Copyright © 2021 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mouzaki M, Bronsky J, Gupte G, et al. Nutritional Support of Children With Chronic Liver Diseases: A Joint Position Paper of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2019;69:498–511. - PubMed
-
- Utterson EC, Shepherd RW, Sokol RJ, et al. Biliary atresia: clinical profiles, risk factors, and outcomes of 755 patients listed for liver transplantation. J Pediatr 2005;147(2):180–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical