Triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol predict coronary heart disease risk in patients with stable angina
- PMID: 34671067
- PMCID: PMC8528835
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-00020-3
Triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol predict coronary heart disease risk in patients with stable angina
Abstract
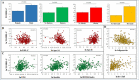
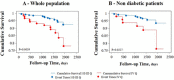
We assessed whether high triglycerides (TG) and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels, expressed by an increased TG/HDL-C ratio, predict coronary atherosclerotic disease (CAD) outcomes in patients with stable angina. We studied 355 patients (60 ± 9 years, 211 males) with stable angina who underwent coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA), were managed clinically and followed for 4.5 ± 0.9 years. The primary composite outcome was all-cause mortality and non-fatal myocardial infarction. At baseline, the proportion of males, patients with metabolic syndrome, diabetes and obstructive CAD increased across TG/HDL-C ratio quartiles, together with markers of insulin resistance, hepatic and adipose tissue dysfunction and myocardial damage, with no difference in total cholesterol or LDL-C. At follow-up, the global CTA risk score (HR 1.06, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.03-1.09, P = 0.001) and the IV quartile of the TG/HDL-C ratio (HR 2.85, 95% CI 1.30-6.26, P < 0.01) were the only independent predictors of the primary outcome. The TG/HDL-C ratio and the CTA risk score progressed over time despite increased use of lipid-lowering drugs and reduction in LDL-C. In patients with stable angina, high TG and low HDL-C levels are associated with CAD related outcomes independently of LDL-C and treatments.Trial registration. EVINCI study: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00979199, registered September 17, 2009; SMARTool study: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04448691, registered June 26, 2020.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, Capodanno D, Barbato E, Funck-Brentano C, Prescott E, Storey RF, Deaton C, Agewall TCS, Dickstein K, Edvardsen T, Escaned J, Gersh BJ, Svitil P, Gilard M, Hasdai D, Hatala R, Mahfoud F, Masip J, Muneretto C, Valgimigli M, Achenbach S, Bax JJ, ESC Scientific Document Group ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes: The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. Heart J. 2020;3:407–477. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz425. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey C, Ceriello A, Delgado V, Federici M, Filippatos G, Grobbee DE, Hansen TB, Huikuri HV, Johansson I, Jüni P, Lettino M, Marx N, Mellbin LG, Östgren CJ, Rocca B, Roffi M, Sattar N, Seferović PM, Sousa-Uva M, Valensi P, Wheeler DC, ESC Scientific Document Group ESC/EASD guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2019;2020(41):255–323. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz486. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ, Drexel H, Hoes AW, Jennings CS, Landmesser U, Pedersen TR, Reiner Z, Riccardi G, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Verschuren WMM, Vlachopoulos C, Wood DA, Zamorano JL, Cooney MT. ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Eur. Heart J. 2016;37:2999–3058. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw272. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castañer O, Pintó X, Subirana I, Amor AJ, Ros E, Hernáez Á, Martínez-González MÁ, Corella D, Salas-Salvadó J, Estruch R, Lapetra J, Gómez-Gracia E, Alonso-Gomez AM, Fiol M, Serra-Majem L, Corbella E, Benaiges D, Sorli JV, Ruiz-Canela M, Babió N, Sierra LT, Ortega E, Fitó M. Remnant cholesterol, not LDL cholesterol, is associated with incident cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76(23):2712–2724. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.10.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

