Genetic transformation and growth index determination of the Larix olgensis LoHDZ2 transcription factor gene in tobacco
- PMID: 34671092
- PMCID: PMC8528859
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-99533-0
Genetic transformation and growth index determination of the Larix olgensis LoHDZ2 transcription factor gene in tobacco
Abstract
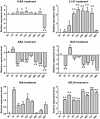
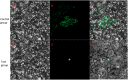
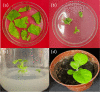
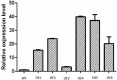
Homeodomain-leucine zippers (HD-Zip) are plant-specific transcription factors that participate in different plant development processes and differentially regulate metabolic processes. LoHDZ2 is an HD-ZipII subfamily transcription factor gene that we identified from a transcriptomic analysis of Larix olgensis. To understand its function, we built a LoHDZ2 expression vector and then inserted it into tobacco by genetic transformation. Transgenic plants were identified at the DNA and RNA levels. Phenotypic index analysis of transgenic tobacco showed dwarfed growth with larger leaves and earlier flowering than the wild type. LoHDZ2 was expressed differently after hormone treatment with IAA, MeJA and 2,4-D. The results suggested that LoHDZ2 may respond to hormones and be involved in regulating growth and metabolism. These results helped us better understand the function of LoHDZ2 and provided a candidate gene for Larix olgensis molecular breeding.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Isolation and functional analysis of the Larix olgensis LoNAC3 transcription factor gene.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Sep 28;24(1):881. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05619-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39342102 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic transformation of LoHDZ2 and analysis of its function to enhance stress resistance in Larix olgensis.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 27;12(1):12831. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17191-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35896808 Free PMC article.
-
The HD-Zip gene ATHB6 in Arabidopsis is expressed in developing leaves, roots and carpels and up-regulated by water deficit conditions.Plant Mol Biol. 1999 Aug;40(6):1073-83. doi: 10.1023/a:1006267013170. Plant Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10527431
-
HD-ZIP Gene Family: Potential Roles in Improving Plant Growth and Regulating Stress-Responsive Mechanisms in Plants.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 17;12(8):1256. doi: 10.3390/genes12081256. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant transcription factors from the homeodomain-leucine zipper family I. Role in development and stress responses.IUBMB Life. 2017 May;69(5):280-289. doi: 10.1002/iub.1619. Epub 2017 Mar 24. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28337836 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and functional analysis of the Larix olgensis LoNAC3 transcription factor gene.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Sep 28;24(1):881. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05619-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39342102 Free PMC article.
-
The SEPALLATA-like gene HrSEP1 in Hippophae rhamnoides regulates flower development by interacting with other MADS-box subfamily genes.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 29;15:1503346. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1503346. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39944949 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic transformation of LoHDZ2 and analysis of its function to enhance stress resistance in Larix olgensis.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 27;12(1):12831. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17191-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35896808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu, Y. The molecular mechanism of plant hormone ABSCISIC ACID regulates suberin biosynthesis in arabidopsis thalana. 2015.
-
- Tang, X., et al. A single transcript CRISPR-Cas9 system for multiplex genome editing in plants, 2019. p. 75–82. - PubMed
-
- Xue W, et al. Experimental study on soil fire temperature field of harvested site of Larix olgensis plantation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019;30(3):785–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

