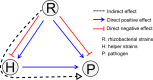
Indirect reduction of Ralstonia solanacearum via pathogen helper inhibition
- PMID: 34671104
- PMCID: PMC8857195
- DOI: 10.1038/s41396-021-01126-2
Indirect reduction of Ralstonia solanacearum via pathogen helper inhibition
Abstract
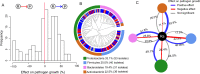
The rhizosphere microbiome forms a first line of defense against soilborne pathogens. To date, most microbiome enhancement strategies have relied on bioaugmentation with antagonistic microorganisms that directly inhibit pathogens. Previous studies have shown that some root-associated bacteria are able to facilitate pathogen growth. We therefore hypothesized that inhibiting such pathogen helpers may help reduce pathogen densities. We examined tripartite interactions between a model pathogen, Ralstonia solanacearum, two model helper strains and a collection of 46 bacterial isolates recovered from the tomato rhizosphere. This system allowed us to examine the importance of direct (effects of rhizobacteria on pathogen growth) and indirect (effects of rhizobacteria on helper growth) pathways affecting pathogen growth. We found that the interaction between rhizosphere isolates and the helper strains was the major determinant of pathogen suppression both in vitro and in vivo. We therefore propose that controlling microbiome composition to prevent the growth of pathogen helpers may become part of sustainable strategies for pathogen control.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures