Improvement of Non-motor Symptoms and Quality of Life After Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Dystonia: A 1-Year Follow-Up
- PMID: 34671310
- PMCID: PMC8520898
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.717239
Improvement of Non-motor Symptoms and Quality of Life After Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Dystonia: A 1-Year Follow-Up
Abstract
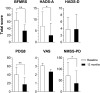
Introduction: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a treatment option for refractory dystonia's motor symptoms, while its non-motor symptoms (NMS) have been less systematically assessed. We aimed to describe the effects of DBS on NMS in refractory generalized inherited/idiopathic dystonia prospectively. Methods: We evaluated patients before and 1 year after DBS surgery and applied the following scales: Burke-Fahn-Marsden Rating Scale (BFMRS), NMS Scale for Parkinson's Disease (NMSS-PD), Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire-8, short-form Brief Pain Inventory (BPI), Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory (NPSI), and short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ). Results: Eleven patients (38.35 ± 11.30 years) underwent surgery, all with generalized dystonia. Motor BFMRS subscore was 64.36 ± 22.94 at baseline and 33.55 ± 17.44 1 year after DBS surgery (47.9% improvement, p = 0.003). NMSS-PD had a significant change 12 months after DBS, from 70.91 ± 59.07 to 37.18 ± 55.05 (47.5% improvement, p = 0.013). NMS changes were mainly driven by changes in the gastrointestinal (p = 0.041) and miscellaneous domains (p = 0.012). Seven patients reported chronic pain before DBS and four after it. BPI's severity and interference scores were 4.61 ± 2.84 and 4.12 ± 2.67, respectively, before surgery, and 2.79 ± 2.31 (0.00-6.25) and 1.12 ± 1.32 (0.00-3.00) after, reflecting a significant improvement (p = 0.043 and p = 0.028, respectively). NPSI score was 15.29 ± 13.94 before, while it was reduced to 2.29 ± 2.98 afterward (p = 0.028). MPQ's total score was 9.00 ± 3.32 before DBS, achieving 2.71 ± 2.93 after (p = 0.028). Conclusions: DBS improves NMS in generalized inherited/idiopathic dystonia, including chronic pain.
Keywords: deep brain stimulation; dystonia; non-motor symptoms; pain; quality of life.
Copyright © 2021 Listik, Cury, Casagrande, Listik, Arnaut, Santiago, Da Silva, Galhardoni, Machado, Almeida, Barbosa, Teixeira and De Andrade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of deep brain stimulation on pain and other nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson disease.Neurology. 2014 Oct 14;83(16):1403-9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000887. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 25217059
-
Surgical Management for Dystonia: Efficacy of Deep Brain Stimulation in the Long Term.Neurol Int. 2021 Aug 2;13(3):371-386. doi: 10.3390/neurolint13030037. Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 34449699 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for treatment of non-dYT1 generalized dystonia and choreoathetosis: 2-year follow up.J Neurosurg. 2003 Apr;98(4):785-92. doi: 10.3171/jns.2003.98.4.0785. J Neurosurg. 2003. PMID: 12691403
-
Early deep brain stimulation in patients with myoclonus-dystonia syndrome.J Clin Neurosci. 2016 May;27:17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.08.034. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Clin Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26810467 Review.
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Deep Brain Stimulation for Pediatric Dystonia.Pediatr Neurosurg. 2022;57(4):225-237. doi: 10.1159/000524577. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35439762 Review.
Cited by
-
A decision support system based on recurrent neural networks to predict medication dosage for patients with Parkinson's disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 10;14(1):8424. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59179-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38600209 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha Synuclein Toxicity and Non-Motor Parkinson's.Cells. 2024 Jul 27;13(15):1265. doi: 10.3390/cells13151265. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, et al. . French stimulation du pallidum interne dans la dystonie study, bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:459–67. 10.1056/NEJMoa042187 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

