Evaluation of Angiogenesis and Pathological Classification of Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma by Dynamic MR Imaging for E-Healthcare
- PMID: 34671450
- PMCID: PMC8523230
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8666498
Evaluation of Angiogenesis and Pathological Classification of Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma by Dynamic MR Imaging for E-Healthcare
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Evaluation of Angiogenesis and Pathological Classification of Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma by Dynamic MR Imaging for E-Healthcare.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9789030. doi: 10.1155/2023/9789030. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37946889 Free PMC article.
Abstract
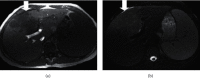
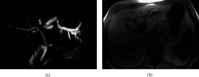
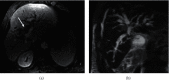
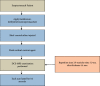
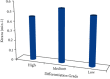
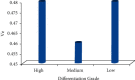
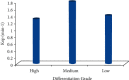
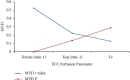
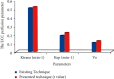
For staging cholangiocarcinoma and determining respectability, MR is an accurate noninvasive method which provides size of tumor and vascular patency information. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is a noninvasive inspection method for evaluating the vascular structure and functional characteristics of tumor tissue. However, some limitations should be noted about the technology. At present, the technology cannot be used alone, which is just an assisted method during the conventional MRI examination. 50 ECC patients, admitted to Indira Gandhi Medical College and Hospital between 2016 and 2019, were selected as research subjects. They were classified pathologically according to the Steiner classification system. After image processing, regions of interest (ROIs) were selected from the image to measure the rate constant (Kep), extravascular space volume fraction (Ve), and tissue volume transfer constant (Ktrans). There were 15 cases with highly differentiated carcinoma, 23 cases with moderately differentiated carcinoma, and 12 cases with lowly differentiated carcinoma. Non-VEGF expression was noted in 21 cases, with low expression noted in 15 cases, moderate expression noted in 14 cases, and no high expression case noted. The relevant parameters in the dynamic MRI image can quantitatively reflect the angiogenesis and pathological classification of ECC, which is suggested in the clinical treatment of ECC. The Ktrans, Kep, and Ve values of the ECC patients were all not associated with the pathological classification, with no significant difference (P < 0.05). Besides, due to the fact that the patient cannot completely hold his breath, the air leak reduces the image quality.
Copyright © 2021 Jinyun Tan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Thakur A., Talluri S. R. Comparative analysis on pulse compression with classical orthogonal polynomials for optimized time-bandwidth product. Ain Shams Engineering Journal . 2018;9(4):1791–1797. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2017.01.003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

