Small RNAs in epigenetic inheritance: from mechanisms to trait transmission
- PMID: 34671979
- PMCID: PMC9298081
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14210
Small RNAs in epigenetic inheritance: from mechanisms to trait transmission
Abstract
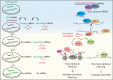
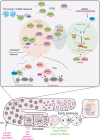
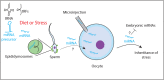
Inherited information is transmitted to progeny primarily by the genome through the gametes. However, in recent years, epigenetic inheritance has been demonstrated in several organisms, including animals. Although it is clear that certain post-translational histone modifications, DNA methylation, and noncoding RNAs regulate epigenetic inheritance, the molecular mechanisms responsible for epigenetic inheritance are incompletely understood. This review focuses on the role of small RNAs in transmitting epigenetic information across generations in animals. Examples of documented cases of transgenerational epigenetic inheritance are discussed, from the silencing of transgenes to the inheritance of complex traits, such as fertility, stress responses, infections, and behavior. Experimental evidence supporting the idea that small RNAs are epigenetic molecules capable of transmitting traits across generations is highlighted, focusing on the mechanisms by which small RNAs achieve such a function. Just as the role of small RNAs in epigenetic processes is redefining the concept of inheritance, so too our understanding of the molecular pathways and mechanisms that govern epigenetic inheritance in animals is radically changing.
Keywords: RNA interference; epigenetics; gene regulation; gene silencing; miRNAs; piRNAs; small RNAs; transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.
© 2021 The Authors. FEBS Letters published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures
References
-
- Miska EA and Ferguson‐Smith AC (2016) Transgenerational inheritance: models and mechanisms of non–DNA sequence–based inheritance. Science 354, 59–63. - PubMed
-
- Skvortsova K, Iovino N and Bogdanović O (2018) Functions and mechanisms of epigenetic inheritance in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19, 774–790. - PubMed
-
- Parry A, Rulands S and Reik W (2021) Active turnover of DNA methylation during cell fate decisions. Nat Rev Genet 22, 59–66. - PubMed
-
- Atlasi Y and Stunnenberg HG (2017) The interplay of epigenetic marks during stem cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet 18, 643–658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

