The Significance of Alliance Networks in Research and Development of Digital Health Products for Diabetes: Observational Study
- PMID: 34673525
- PMCID: PMC8569533
- DOI: 10.2196/32446
The Significance of Alliance Networks in Research and Development of Digital Health Products for Diabetes: Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Digital health has been advancing owing to technological progress by means of smart devices and artificial intelligence, among other developments. In the field of diabetes especially, there are many active use cases of digital technology supporting the treatment of diabetes and improving lifestyle. In the innovation ecosystem, new alliance networks are formed not only by medical device companies and pharmaceutical companies, but also by information and communications technology companies and start-ups. While understanding and utilizing the network structure is important to increase the competitive advantage of companies, there is a lack of previous research describing the structure of alliance networks and the factors that lead to their formation in digital health.
Objective: The aim of this study was to explore the significance of alliance networks, focusing on digital health for diabetes, in effectively implementing processes, from the research and development of products or services to their launch and market penetration.
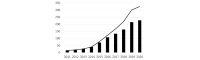
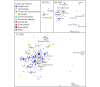
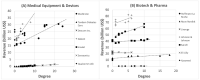
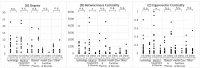
Methods: First, we listed the companies and contracts related to digital health for diabetes, visualized the change in the number of companies and the connections between companies in each industry, and analyzed the overview of the network. Second, we calculated the degree, betweenness centrality, and eigenvector centrality of each company in each year. Next, we analyzed the relationship between network centrality and market competitiveness by using annual sales as a parameter of company competitiveness. We also compared the network centrality of each company by industry or headquarters location (or both) and analyzed the characteristics of companies with higher centrality. Finally, we analyzed the relationship between network centrality and the number of products certified or approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Results: We found the degree centrality of companies was correlated with an increase in their sales. The betweenness and eigenvector centralities of medical devices companies located in the United States were significantly higher than those outside the United States (P=.04 and .005, respectively). Finally, the degree, betweenness, and eigenvector centralities were correlated with an increase in the number of Class III, but not of Class I nor II, medical device products.
Conclusions: These findings give rise to new insights into industry ecosystem for digital health and its requirement and expect a contribution to research and development practices in the field of digital health.
Keywords: alliance; diabetes; digital health; network; wearable device.
©Satoru Kikuchi, Kota Kodama, Shintaro Sengoku. Originally published in JMIR Diabetes (https://diabetes.jmir.org), 21.10.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: SK is an employee of Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Early achievements of the Danish pharmaceutical industry--8. Lundbeck].Theriaca. 2016;(43):9-61. Theriaca. 2016. PMID: 27491172 Danish.
-
A new measure of centrality for brain networks.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 16;5(8):e12200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012200. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808943 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib: CP 358774, NSC 718781, OSI 774, R 1415.Drugs R D. 2003;4(4):243-8. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304040-00006. Drugs R D. 2003. PMID: 12848590
-
New ways of insulin delivery.Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011 Feb;(170):31-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02577.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011. PMID: 21323811 Review.
-
New ways of insulin delivery.Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2010 Feb;(166):29-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02276.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2010. PMID: 20377662 Review.
Cited by
-
MedTech start-ups: A comprehensive scoping review of current research trends and future directions.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 6;19(8):e0307959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307959. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39106273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Digital Health Center of Excellence. [2021-10-04]. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/digital-health .
-
- The Power of Digitalizing Health Care. [2021-10-04]. https://cdn0.scrvt.com/39b415fb07de4d9656c7b516d8e2d907/1800000004474496... .
-
- Fleming GA, Petrie JR, Bergenstal RM, Holl RW, Peters AL, Heinemann L. Diabetes digital app technology: benefits, challenges, and recommendations. A consensus report by the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Diabetes Technology Working Group. Diabetologia. 2020 Feb;63(2):229–241. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05034-1.10.1007/s00125-019-05034-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Who Are the Digital Diabetes Market Players that Transform the Diabetes Industry? [2021-10-04]. https://research2guidance.com/digital-diabetes-industry-is-growing-quick...
-
- Kerr D, King F, Klonoff DC. Digital Health Interventions for Diabetes: Everything to Gain and Nothing to Lose. Diabetes Spectr. 2019 Aug;32(3):226–230. doi: 10.2337/ds18-0085. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/31462878 226 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

